Anatomy of Watermelon: A Deeper Look
-
Table of Contents
- Watermelon Anatomy: Exploring the Fruit’s Inner Workings
- The Exterior: Rind and Skin
- The Flesh: Color, Texture, and Composition
- The Seeds: Types and Functions
- Seedless Watermelons: A Horticultural Achievement
- Flowering and Pollination: The Growth Cycle
- Nutritional Benefits: A Healthy Choice
- Conclusion: The Wonders of Watermelon Anatomy
- Enhance Your Diet with ETprotein’s Watermelon Seed Protein
Watermelon Anatomy: Exploring the Fruit’s Inner Workings
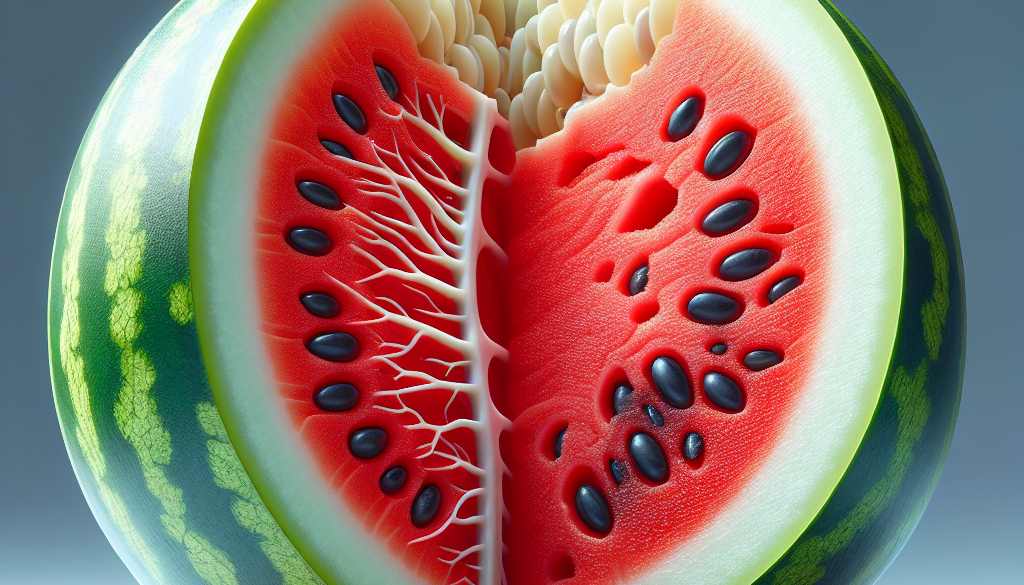
Watermelons are a staple of summer picnics and barbecues, known for their refreshing taste and hydrating properties. But beyond their delicious flavor and thirst-quenching abilities, watermelons are fascinating fruits with a complex anatomy. In this article, we’ll take a deeper look at the structure of watermelons, exploring each part from the rind to the seeds, and uncovering the science behind their growth and development.
The Exterior: Rind and Skin
The watermelon’s exterior is made up of a thick rind that encases the fruit. This rind is composed of two layers: the outer skin and the inner white rind, or exocarp and mesocarp, respectively. The outer skin is typically green with darker green stripes, although some varieties may have different patterns or colors. The skin’s primary function is to protect the inner flesh from pests and environmental factors.
The inner white rind, while not typically consumed, plays a crucial role in the fruit’s development. It acts as a storage area for nutrients and water, helping to keep the flesh juicy and sweet. The thickness of the rind can vary depending on the watermelon variety and growing conditions.
The Flesh: Color, Texture, and Composition
The flesh, or endocarp, is the part of the watermelon that is most commonly consumed. It ranges in color from deep red to pink, orange, yellow, or even white, depending on the variety. The flesh’s color is due to the presence of lycopene in red and pink varieties, which is also an antioxidant.
The texture of the flesh is crisp and juicy, a result of its high water content, which can be up to 92%. This high water content makes watermelon an excellent fruit for hydration. The flesh also contains natural sugars, vitamins (such as vitamin A, B6, and C), and minerals, making it a nutritious snack option.
The Seeds: Types and Functions
Watermelon seeds are found embedded in the flesh and come in two main types: hard black seeds and soft white seeds, also known as seed coats. The black seeds are mature seeds that can be dried and planted to grow new watermelon plants. They are also edible and can be roasted for a crunchy snack, rich in protein, healthy fats, and minerals.
Soft white seeds are immature seeds that have not fully developed. These seeds are often found in seedless watermelon varieties, which are not truly seedless but have been bred to produce non-viable seeds that remain soft and edible.
Seedless Watermelons: A Horticultural Achievement
Seedless watermelons are a result of crossbreeding different watermelon varieties with altered chromosome numbers. This process creates a sterile fruit that does not produce mature seeds. Seedless watermelons have gained popularity for their convenience, as they save consumers the effort of removing seeds before eating.
Flowering and Pollination: The Growth Cycle
Watermelons start their life cycle as flowers on the watermelon plant. These flowers are either male or female, with the male flowers appearing first. Pollination is crucial for fruit development, and it typically occurs with the help of bees transferring pollen from male to female flowers.
Once pollinated, the female flower’s ovary begins to swell and develop into the fruit we recognize as a watermelon. The growth cycle from pollination to harvest can take anywhere from 65 to 90 days, depending on the variety and growing conditions.
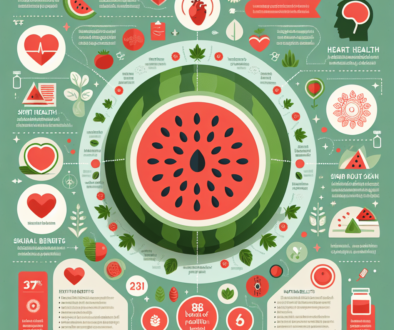
Nutritional Benefits: A Healthy Choice
Watermelons are not only delicious but also offer a range of health benefits. They are low in calories and contain no fat, making them an ideal choice for those looking to maintain a healthy weight. The high water content helps with hydration, while the presence of vitamins and antioxidants supports overall health.
Lycopene, in particular, has been studied for its potential to reduce the risk of certain types of cancer and cardiovascular diseases. Watermelons also contain citrulline, an amino acid that may improve blood flow and reduce muscle soreness.
Conclusion: The Wonders of Watermelon Anatomy
The anatomy of a watermelon is a testament to the intricacies of nature’s design. From the protective rind to the nutrient-rich flesh and seeds, each part of the watermelon serves a purpose in the fruit’s growth and development. Understanding the anatomy of watermelons not only enhances our appreciation for this summer fruit but also highlights the importance of each component in contributing to its nutritional value.
Whether enjoyed fresh off the rind, blended into a smoothie, or incorporated into a salad, watermelons are a versatile and healthy addition to any diet. Their complex anatomy ensures that every bite is packed with hydration, flavor, and nutrients.
Enhance Your Diet with ETprotein’s Watermelon Seed Protein
If you’re looking to incorporate the nutritional benefits of watermelon into your diet beyond the fruit itself, consider ETprotein’s watermelon seed protein. This product is derived from high-quality watermelon seeds, providing a plant-based protein source that’s perfect for vegans and those with dietary restrictions.
ETprotein’s watermelon seed protein is an excellent addition to smoothies, shakes, and baked goods, offering a neutral taste and a boost of protein. It’s non-GMO, allergen-free, and suitable for a wide range of applications, from sports nutrition to health and wellness products.
For those interested in exploring the benefits of watermelon seed protein and other plant-based proteins, ETprotein is a reliable supplier that can meet your needs. With a commitment to quality and customer satisfaction, ETprotein is your go-to source for organic bulk vegan protein.
About ETprotein:
ETprotein, a reputable watermelon seed protein Chinese factory manufacturer and supplier, is renowned for producing, stocking, exporting, and delivering the highest quality organic bulk vegan protein and plant proteins. They include Organic rice protein, clear rice protein, pea protein, clear pea protein, watermelon seed protein, pumpkin seed protein, sunflower seed protein, mung bean protein, peanut protein etc. Their offerings, characterized by a neutral taste, non-GMO, allergen-free attributes, cater to a diverse range of industries. They serve nutraceutical, pharmaceutical, cosmeceutical, veterinary, as well as food and beverage finished product distributors, traders, and manufacturers across Europe, USA, Canada, Australia, Thailand, Japan, Korea, Brazil, and Chile, among others.
ETprotein specialization includes exporting and delivering tailor-made protein powder and finished nutritional supplements. Their extensive product range covers sectors like Food and Beverage, Sports Nutrition, Weight Management, Dietary Supplements, Health and Wellness Products, and Infant Formula, ensuring comprehensive solutions to meet all your protein needs.
As a trusted company by leading global food and beverage brands and Fortune 500 companies, ETprotein reinforces China’s reputation in the global arena. For more information or to sample their products, please contact them and email sales(at)ETprotein.com today.