Are Peanuts Seeds? Unpacking The Botanical Truth
-
Table of Contents
- Are Peanuts Seeds? Unpacking the Botanical Truth
- Understanding the Botanical Basics
- What Exactly Are Peanuts?
- The Botanical Classification of Peanuts
- Nutritional Profile and Benefits of Peanuts
- Peanuts in Agriculture and Economy
- Case Studies and Statistics
- Conclusion: The Veracity of Peanuts as Seeds
- Discover ETprotein’s High-Quality Peanut Protein Products
Are Peanuts Seeds? Unpacking the Botanical Truth

When it comes to understanding the botanical world, there are often misconceptions and misunderstandings about the classification of various plant parts. One such confusion revolves around peanuts. Are they nuts, legumes, or seeds? This article aims to unpack the botanical truth about peanuts and provide a clear understanding of their classification.
Understanding the Botanical Basics
Before diving into the specifics of peanuts, it’s essential to grasp some fundamental botanical concepts. Plants reproduce through seeds, which are embryonic plants enclosed in a protective outer covering. Seeds are the product of the fertilized ovule of flowering plants and are designed to develop into a new plant.
What Exactly Are Peanuts?
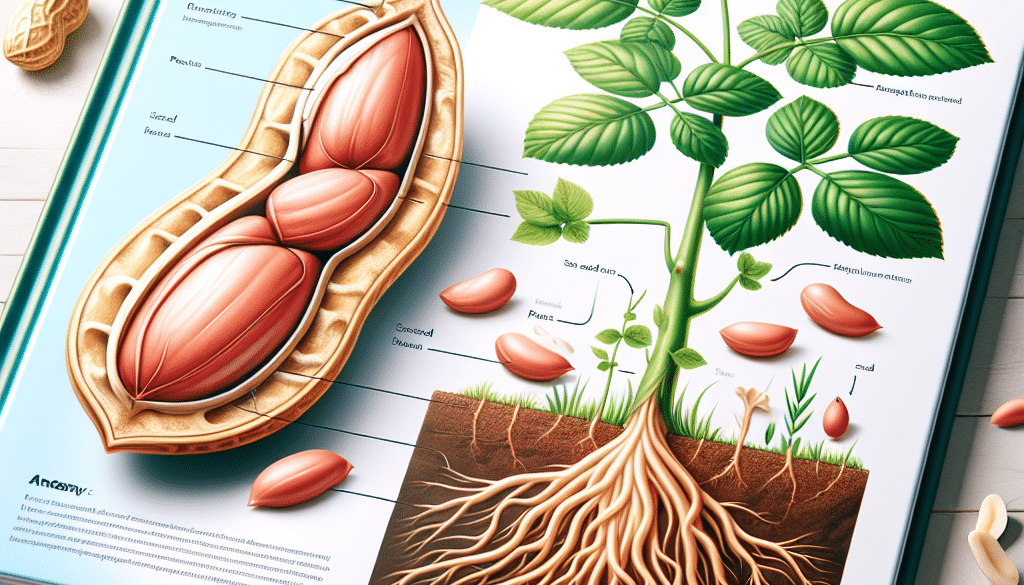
Peanuts, contrary to their name, are not true nuts. In the botanical sense, a nut is a hard-shelled pod that contains both the fruit and seed of the plant, where the fruit does not open to release the seed to the world. Examples of true nuts include acorns and chestnuts. Peanuts, on the other hand, are legumes. Legumes are a type of fruit that splits open naturally to release seeds when they mature. Other members of the legume family include beans, lentils, and peas.
The Botanical Classification of Peanuts
Peanuts, scientifically known as Arachis hypogaea, are indeed seeds. They are the seeds of a leguminous plant and grow in a fascinating manner. Unlike most plants, the peanut plant flowers above the ground, but the peanuts themselves develop below the ground. This process is known as geocarpy, which is a unique characteristic of the peanut plant.
- The peanut plant flowers above the soil.
- After pollination, the flower stalk elongates and bends towards the ground.
- The developing ovary, or peg, is pushed into the ground.
- The peanut matures underground, enclosed in a thin shell that is the fruit of the plant.
- The shell contains the seeds, which we commonly refer to as peanuts.
Nutritional Profile and Benefits of Peanuts
Peanuts are not only a delicious snack but also packed with nutritional benefits. They are an excellent source of protein, healthy fats, vitamins, and minerals. Here’s a closer look at the nutritional profile of peanuts:
- Rich in monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats
- Good source of protein
- Contains fiber, which aids in digestion
- High in vitamins E, B6, and niacin
- Contains minerals like magnesium, phosphorus, and potassium
- Source of antioxidants
Regular consumption of peanuts has been linked to various health benefits, including a reduced risk of heart disease, control of blood sugar levels, and even a lower risk of gallstones.
Peanuts in Agriculture and Economy
The cultivation of peanuts plays a significant role in agriculture and the economy. They are grown in tropical and subtropical regions around the world, with China, India, and the United States being the top producers. Peanuts are used in a variety of products, from peanut butter to cooking oil, and even in the production of livestock feed.
Case Studies and Statistics
Research has shown that peanuts can be a sustainable crop, contributing to economic development in rural areas. For instance, in countries like Senegal and Ghana, peanut farming has been a critical source of income for many families. Additionally, the introduction of improved peanut farming techniques has increased yields and quality, further boosting the economic impact of this crop.
Conclusion: The Veracity of Peanuts as Seeds
In conclusion, peanuts are indeed seeds from a botanical perspective. They are the edible seeds of a legume plant and are a valuable crop both nutritionally and economically. Understanding the true nature of peanuts can enhance our appreciation for this versatile and nutritious food source.
Discover ETprotein’s High-Quality Peanut Protein Products
If you’re looking for a reliable source of plant-based protein, ETprotein offers a range of products that include peanut protein. Their commitment to quality ensures that you receive a product that is not only high in protein but also has a neutral taste and is non-GMO and allergen-free. Whether you’re in the food and beverage industry or looking for dietary supplements, ETprotein has the protein solutions to meet your needs.
About ETprotein:
ETprotein, a reputable protein Chinese factory manufacturer and supplier, is renowned for producing, stocking, exporting, and delivering the highest quality organic bulk vegan protein and plant proteins. They include Organic rice protein, clear rice protein, pea protein, clear pea protein, pumpkin seed protein, sunflower seed protein, mung bean protein, peanut protein etc. Their offerings, characterized by a neutral taste, non-GMO, allergen-free attributes, cater to a diverse range of industries. They serve nutraceutical, pharmaceutical, cosmeceutical, veterinary, as well as food and beverage finished product distributors, traders, and manufacturers across Europe, USA, Canada, Australia, Thailand, Japan, Korea, Brazil, and Chile, among others.
ETprotein specialization includes exporting and delivering tailor-made protein powder and finished nutritional supplements. Their extensive product range covers sectors like Food and Beverage, Sports Nutrition, Weight Management, Dietary Supplements, Health and Wellness Products, and Infant Formula, ensuring comprehensive solutions to meet all your protein needs.
As a trusted company by leading global food and beverage brands and Fortune 500 companies, ETprotein reinforces China’s reputation in the global arena. For more information or to sample their products, please contact them and email sales(at)ETprotein.com today.