Gamma Aminobutyric Acid Mechanism of Action
-
Table of Contents
- Gamma Aminobutyric Acid: Unveiling Its Mechanism of Action
- Understanding GABA’s Role in the Nervous System
- The Two Types of GABA Receptors
- The Biochemical Pathway of GABA
- Regulatory Functions of GABA
- GABA’s Mechanism of Action: A Closer Look
- Examples and Case Studies
- Therapeutic Implications and Future Directions
- Conclusion: Key Takeaways on GABA’s Mechanism of Action
- Discover High-Quality Proteins with ETprotein
Gamma Aminobutyric Acid: Unveiling Its Mechanism of Action

GABA, or Gamma Aminobutyric Acid, is a crucial neurotransmitter in the human brain, playing a pivotal role in regulating neuronal excitability throughout the nervous system. As the primary inhibitory neurotransmitter, GABA’s mechanism of action is essential for maintaining the delicate balance of neural activity. This article delves into the intricacies of GABA’s function, exploring how it influences brain activity and the implications for health and disease.
Understanding GABA’s Role in the Nervous System
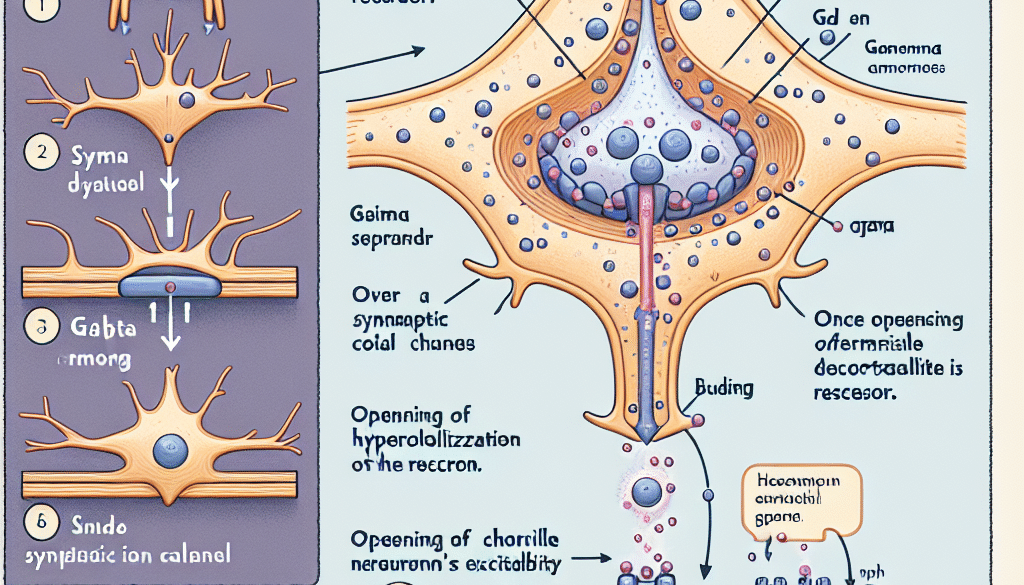
GABA is synthesized in the brain from glutamate, an excitatory neurotransmitter, through the action of the enzyme glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD). Once released into the synaptic cleft, GABA interacts with its receptors on the postsynaptic neuron to exert its inhibitory effects.
The Two Types of GABA Receptors
- GABAA Receptors: These are ionotropic receptors that function as chloride channels. When GABA binds to these receptors, they open to allow chloride ions to flow into the neuron, leading to hyperpolarization and a decrease in the likelihood of the neuron firing an action potential.
- GABAB Receptors: These are metabotropic receptors that work through G-proteins and second messengers. Activation of GABAB receptors leads to the opening of potassium channels and the closing of calcium channels, further contributing to the inhibition of neuronal firing.
The Biochemical Pathway of GABA
The synthesis, release, and reuptake of GABA are tightly regulated processes within the central nervous system. After GABA has exerted its effects, it is removed from the synaptic cleft through reuptake into neurons and glial cells by GABA transporters (GATs). It can then be recycled or metabolized by the enzyme GABA transaminase (GABA-T).
Regulatory Functions of GABA
GABA’s inhibitory action is vital for various brain functions, including:
- Mood regulation
- Stress response
- Seizure threshold
- Sleep cycles
Disruptions in GABAergic signaling have been implicated in numerous neurological and psychiatric disorders, such as epilepsy, anxiety, depression, and insomnia.
GABA’s Mechanism of Action: A Closer Look
At the core of GABA’s mechanism of action is its ability to reduce neuronal excitability. This is achieved through the following steps:
- Synthesis of GABA from glutamate in the presynaptic neuron.
- Storage of GABA in synaptic vesicles.
- Release of GABA into the synaptic cleft upon neuronal activation.
- Binding of GABA to its receptors on the postsynaptic neuron.
- Consequent opening or closing of ion channels, leading to changes in the postsynaptic neuron’s membrane potential.
- Termination of the GABA signal through reuptake or metabolism.
Examples and Case Studies
Research has shown that alterations in GABAergic signaling can lead to various clinical conditions. For instance, in epilepsy, a deficiency in GABA or dysfunction in GABA receptors can lead to uncontrolled neuronal firing and seizures. Benzodiazepines, a class of drugs used to treat anxiety and seizures, work by enhancing the effects of GABA at the GABAA receptor, demonstrating the therapeutic potential of modulating GABAergic activity.
Therapeutic Implications and Future Directions
The understanding of GABA’s mechanism of action has significant implications for the development of new treatments for neurological and psychiatric disorders. Future research is focused on:
- Developing selective GABA receptor modulators to minimize side effects.
- Exploring gene therapy to correct GABAergic deficits.
- Investigating the role of GABA in neurodevelopmental disorders.
Conclusion: Key Takeaways on GABA’s Mechanism of Action
In summary, GABA’s mechanism of action is a fundamental aspect of neural communication, ensuring that our nervous system operates within a balanced state. Its inhibitory effects are crucial for preventing overexcitation and maintaining mental and neurological health. Understanding GABA’s role opens avenues for treating various disorders and improving the quality of life for those affected by GABAergic dysregulation.
Discover High-Quality Proteins with ETprotein
If you’re looking for premium protein products, ETprotein offers an extensive range of organic bulk vegan proteins that can support your health and wellness goals. Their products, including L-(+)-Ergothioneine, are of the highest purity and cater to various industries, ensuring that you receive only the best for your nutritional needs.
Whether you’re a distributor, trader, or manufacturer, ETprotein’s offerings can enhance your product line and provide your customers with the benefits of high-quality proteins. Contact ETprotein today to explore their range and find the perfect solution for your protein requirements.
About ETprotein:
ETprotein, a reputable protein and L-(+)-Ergothioneine (EGT) Chinese factory manufacturer and supplier, is renowned for producing, stocking, exporting, and delivering the highest quality organic bulk vegan proteins and L-(+)-Ergothioneine. They include Organic rice protein, clear rice protein, pea protein, clear pea protein, watermelon seed protein, pumpkin seed protein, sunflower seed protein, mung bean protein, peanut protein, and L-(+)-Ergothioneine EGT Pharmaceutical grade, L-(+)-Ergothioneine EGT food grade, L-(+)-Ergothioneine EGT cosmetic grade, L-(+)-Ergothioneine EGT reference grade and L-(+)-Ergothioneine EGT standard. Their offerings, characterized by a neutral taste, non-GMO, allergen-free attributes, with L-(+)-Ergothioneine purity over 98%, 99%, cater to a diverse range of industries. They serve nutraceutical, pharmaceutical, cosmeceutical, veterinary, as well as food and beverage finished product distributors, traders, and manufacturers across Europe, USA, Canada, Australia, Thailand, Japan, Korea, Brazil, and Chile, among others.
ETprotein specialization includes exporting and delivering tailor-made protein powder and finished nutritional supplements. Their extensive product range covers sectors like Food and Beverage, Sports Nutrition, Weight Management, Dietary Supplements, Health and Wellness Products, and Infant Formula, ensuring comprehensive solutions to meet all your protein needs.
As a trusted company by leading global food and beverage brands and Fortune 500 companies, ETprotein reinforces China’s reputation in the global arena. For more information or to sample their products, please contact them and email sales(at)ETprotein.com today.