Gut-Brain Axis Research Shows Link Between Hunger Hormone and Memory
-
Table of Contents
- Gut-Brain Axis Research: Exploring the Connection Between Hunger Hormones and Memory
- Understanding the Gut-Brain Axis
- The Role of Hunger Hormones
- Linking Hunger Hormones to Memory
- Case Studies and Research Findings
- Implications for Health and Disease Management
- Conclusion: The Future of Gut-Brain Axis Research
- Enhance Your Health with ETprotein’s High-Quality Protein Products
Gut-Brain Axis Research: Exploring the Connection Between Hunger Hormones and Memory
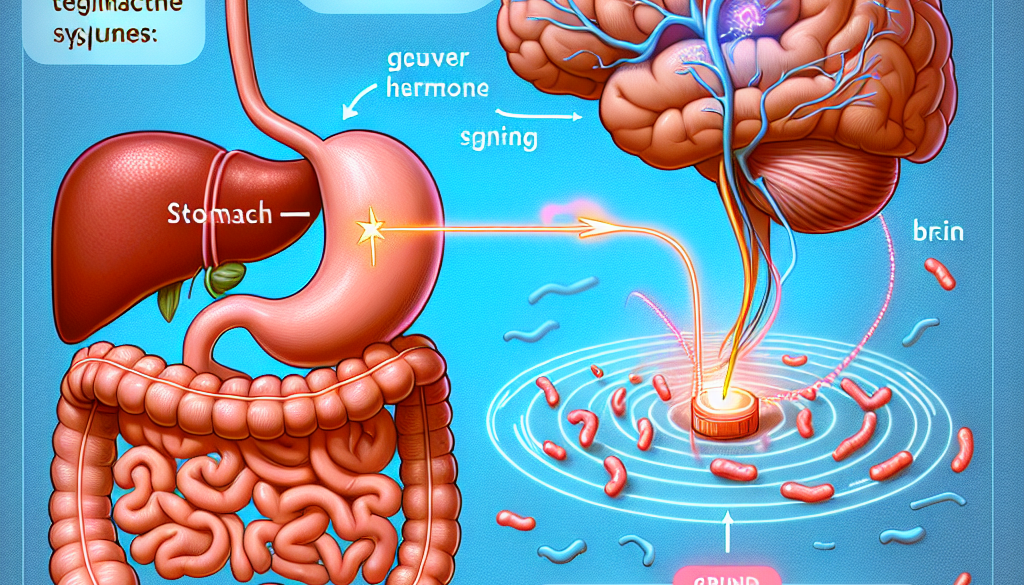
The human body is an intricate network of systems that communicate with each other to maintain homeostasis. One of the most fascinating and complex relationships within this network is the gut-brain axis, a bidirectional communication pathway that links the central nervous system with the gastrointestinal tract. Recent research in this field has uncovered a compelling connection between hunger hormones and memory, shedding light on how our dietary habits and gut health can influence cognitive functions. This article delves into the groundbreaking studies that explore this link, offering insights into the potential implications for health and disease management.
Understanding the Gut-Brain Axis
The gut-brain axis is a term used to describe the communication network that connects your gut and brain. These two organs are linked both physically and biochemically in a number of different ways. Signals from the brain can influence the composition of the gut microbiota, and in turn, the substances produced by the gut microbiota can affect the brain.
- Vagus Nerve: This is one of the biggest nerves connecting the gut and brain. It sends signals in both directions.
- Neurotransmitters: The gut produces a wide range of neurotransmitters, including serotonin, which plays a role in controlling mood and happiness.
- Immune System: The gut’s immune system plays a part in controlling inflammation, which can affect the brain.
- Short-Chain Fatty Acids: These are produced by gut bacteria and have various effects on brain function.
The Role of Hunger Hormones
Hunger hormones such as ghrelin and leptin are key players in appetite regulation and energy balance. Ghrelin, often referred to as the “hunger hormone,” is produced in the stomach and signals the brain to stimulate appetite. Leptin, on the other hand, is known as the “satiety hormone” and is released from fat cells to suppress hunger and signal fullness.
Linking Hunger Hormones to Memory
Recent studies have begun to explore how these hunger hormones might also play a role in cognitive functions, including memory. Research has shown that ghrelin can cross the blood-brain barrier and bind to receptors in the hippocampus, an area of the brain critical for learning and memory. This interaction suggests that ghrelin may influence cognitive functions.
- Ghrelin and Cognitive Function: Studies in rodents have shown that ghrelin can enhance learning and memory. Human studies have also suggested that ghrelin levels are linked to cognitive abilities.
- Leptin and the Brain: Leptin receptors are widely distributed in the brain, including areas involved in memory and learning. Research indicates that leptin may have neuroprotective effects and could play a role in preventing cognitive decline.
Case Studies and Research Findings
Several studies have provided evidence for the connection between hunger hormones and memory. For instance, a study published in the journal “Nature Neuroscience” found that administering ghrelin to rodents enhanced performance in memory tasks. Another study in the “Journal of Clinical Investigation” observed that leptin might reverse cognitive deficits in animal models.
Human studies have also been conducted. A notable example is research that examined the relationship between fasting-induced ghrelin levels and memory performance. The results suggested that individuals with higher ghrelin levels after fasting performed better on memory tests.
Implications for Health and Disease Management
The link between hunger hormones and memory has significant implications for understanding and managing various health conditions:
- Obesity: Since leptin is produced by fat cells, obesity can lead to leptin resistance, which might affect cognitive functions.
- Eating Disorders: Abnormal levels of ghrelin and leptin are often found in individuals with eating disorders, which could impact their cognitive abilities.
- Age-Related Cognitive Decline: As we age, changes in hormone levels could contribute to memory loss. Understanding how hunger hormones affect the brain could lead to new treatments for conditions like Alzheimer’s disease.
Conclusion: The Future of Gut-Brain Axis Research
The burgeoning field of gut-brain axis research is rapidly evolving, with hunger hormones emerging as a key area of interest. The evidence linking hunger hormones like ghrelin and leptin to memory and cognitive function is compelling, offering a new perspective on how our bodies’ signaling molecules influence the brain. As research continues to unravel the complexities of this relationship, we may find novel approaches to treating cognitive disorders and improving mental health through dietary and lifestyle interventions.
Enhance Your Health with ETprotein’s High-Quality Protein Products
Understanding the gut-brain axis and the role of hunger hormones in memory underscores the importance of maintaining a balanced diet and healthy lifestyle. ETprotein offers a range of premium protein products that can support your nutritional needs and contribute to overall well-being. Whether you’re looking to manage your weight, support muscle growth, or simply maintain a healthy diet, ETprotein’s organic and allergen-free proteins are an excellent choice.
About ETprotein:
ETprotein, a reputable protein and L-(+)-Ergothioneine (EGT) Chinese factory manufacturer and supplier, is renowned for producing, stocking, exporting, and delivering the highest quality organic bulk vegan proteins and L-(+)-Ergothioneine. They include Organic rice protein, clear rice protein, pea protein, clear pea protein, watermelon seed protein, pumpkin seed protein, sunflower seed protein, mung bean protein, peanut protein, and L-(+)-Ergothioneine EGT Pharmaceutical grade, L-(+)-Ergothioneine EGT food grade, L-(+)-Ergothioneine EGT cosmetic grade, L-(+)-Ergothioneine EGT reference grade and L-(+)-Ergothioneine EGT standard. Their offerings, characterized by a neutral taste, non-GMO, allergen-free attributes, with L-(+)-Ergothioneine purity over 98%, 99%, cater to a diverse range of industries. They serve nutraceutical, pharmaceutical, cosmeceutical, veterinary, as well as food and beverage finished product distributors, traders, and manufacturers across Europe, USA, Canada, Australia, Thailand, Japan, Korea, Brazil, and Chile, among others.
ETprotein specialization includes exporting and delivering tailor-made protein powder and finished nutritional supplements. Their extensive product range covers sectors like Food and Beverage, Sports Nutrition, Weight Management, Dietary Supplements, Health and Wellness Products, and Infant Formula, ensuring comprehensive solutions to meet all your protein needs.
As a trusted company by leading global food and beverage brands and Fortune 500 companies, ETprotein reinforces China’s reputation in the global arena. For more information or to sample their products, please contact them and email sales(at)ETprotein.com today.