How Are Peanuts Produced: Cultivating Crunchy Crops
-
Table of Contents
- Peanuts Production: Unveiling the Process Behind Crunchy Crops
- The Lifecycle of a Peanut Plant
- Preparing the Field
- Planting and Cultivation
- Harvesting and Processing
- From Farm to Table
- Global Peanut Production: A Snapshot
- Challenges in Peanut Production
- Conclusion: The Crunchy Conclusion
- Discover ETprotein’s Nutritious Protein Products
Peanuts Production: Unveiling the Process Behind Crunchy Crops
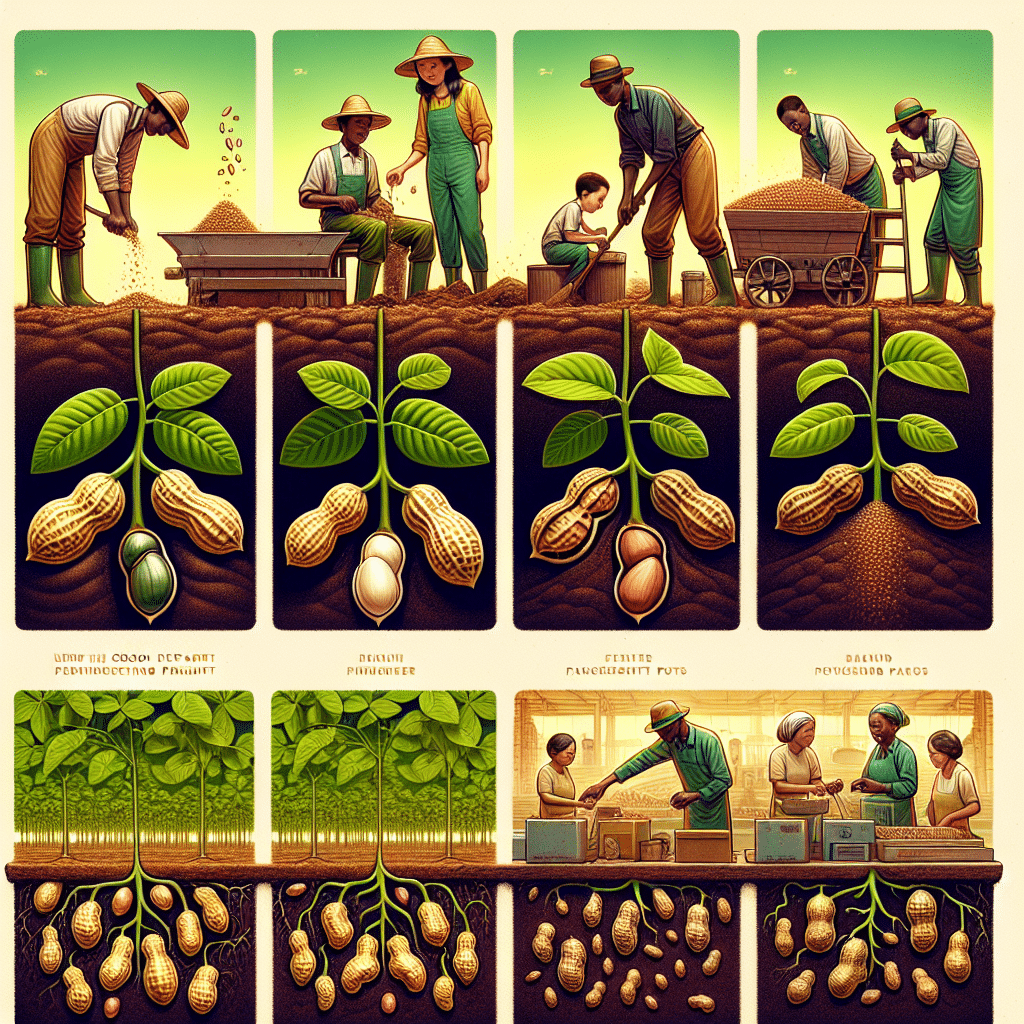
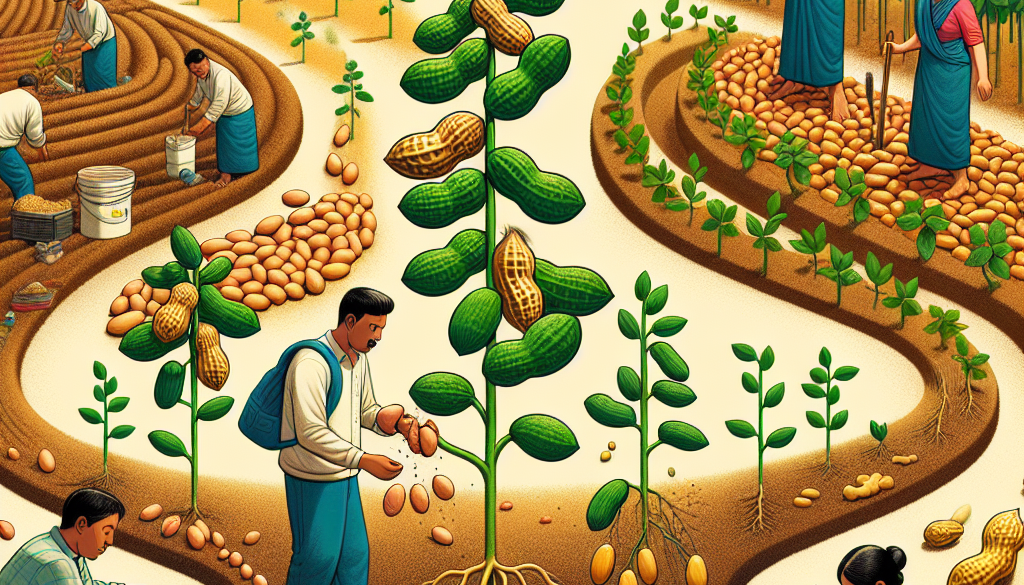
Peanuts, also known as groundnuts, are a staple in diets around the world, revered for their rich flavor and high nutritional value. They play a starring role in a variety of products, from the classic peanut butter to snacks and culinary dishes. But how are these crunchy crops cultivated? This article delves into the fascinating journey of peanuts from the soil to the snack bowl, exploring the meticulous process of peanut production.
The Lifecycle of a Peanut Plant
The peanut plant (Arachis hypogaea) is unique in its growth process. Unlike tree nuts, peanuts grow underground and are classified as legumes. The lifecycle of a peanut plant can be broken down into several stages:
- Germination
- Vegetative Growth
- Flowering
- Pegging
- Maturity
Each stage is critical to the development of a healthy peanut crop. The process begins with germination, where the peanut seed sprouts and sends a shoot upwards while the roots take hold in the soil. During vegetative growth, the plant develops leaves and stems necessary for photosynthesis. Flowering occurs next, and it’s during this stage that the peanut shows its unique reproductive strategy. After pollination, the flower’s stalk elongates and grows towards the ground, burying the fertilized ovary. This process is known as pegging, and it’s where the magic happens: the peanut begins to form underground.
Preparing the Field
Before planting, farmers must ensure that the soil is in optimal condition. Peanuts require well-drained, sandy loam soil with a pH between 5.9 and 7.0. Land preparation involves plowing and harrowing to create a fine, clod-free seedbed. Crop rotation is also a common practice to prevent soil-borne diseases and to maintain soil fertility.
Planting and Cultivation
Peanut planting typically occurs in the spring when the soil temperature reaches at least 65°F (18°C). The seeds are planted about 1 to 1.5 inches deep, with spacing to allow for adequate growth. Farmers use specialized equipment to ensure uniform planting, which is crucial for synchronized crop development.
Throughout the growing season, farmers must manage weeds, pests, and diseases. They may employ integrated pest management (IPM) strategies, which include crop rotation, the use of resistant varieties, and the judicious application of pesticides. Irrigation is also essential, especially during the pegging and pod development stages, to ensure a high-quality yield.
Harvesting and Processing
Harvesting peanuts is a two-step process. First, a digger uproots the plant, shaking off excess soil and inverting the plant to expose the peanuts to the sun. This is followed by a period of field drying, which can take several days. Once the peanuts have dried to the proper moisture content, they are collected using a combine that separates the peanuts from the vines.
After harvest, peanuts undergo further drying to reach a safe storage moisture level. They are then cleaned to remove dirt, vines, and other debris. The peanuts are graded based on size, shape, and quality before being shipped to processing facilities or directly to markets.
From Farm to Table
The journey of peanuts doesn’t end at the farm gate. Once processed, peanuts can be transformed into various products. They can be roasted, blanched, or used to make peanut butter, oil, and flour. Each product requires a specific processing method to ensure the peanuts meet food safety standards and consumer expectations.
Global Peanut Production: A Snapshot
China and India are the world’s largest producers of peanuts, contributing significantly to the global supply. The United States, particularly states like Georgia, Texas, and Alabama, is also a major producer. Advances in agricultural technology, improved seed varieties, and sustainable farming practices have helped increase peanut yields and quality worldwide.
Challenges in Peanut Production
Peanut farmers face several challenges, including climate variability, water scarcity, and the need for sustainable pest management. Research and innovation in peanut breeding are crucial for developing more resilient peanut varieties that can withstand these challenges.
Conclusion: The Crunchy Conclusion
The production of peanuts is a complex process that requires careful attention to detail at every stage. From preparing the soil to harvesting and processing, each step is vital to producing the crunchy, delicious peanuts that consumers enjoy. With ongoing research and sustainable practices, peanut production will continue to thrive, providing a nutritious and versatile crop for generations to come.
Discover ETprotein’s Nutritious Protein Products
If you’re interested in incorporating high-quality protein into your diet or products, consider ETprotein’s range of organic bulk vegan protein and plant proteins. Their peanut protein, along with other plant-based options like rice, pea, and pumpkin seed protein, offers a neutral taste and non-GMO, allergen-free benefits. Ideal for various industries, ETprotein’s products are a testament to their commitment to excellence and sustainability.
About ETprotein:
ETprotein, a reputable protein Chinese factory manufacturer and supplier, is renowned for producing, stocking, exporting, and delivering the highest quality organic bulk vegan protein and plant proteins. They include Organic rice protein, clear rice protein, pea protein, clear pea protein, pumpkin seed protein, sunflower seed protein, mung bean protein, peanut protein etc. Their offerings, characterized by a neutral taste, non-GMO, allergen-free attributes, cater to a diverse range of industries. They serve nutraceutical, pharmaceutical, cosmeceutical, veterinary, as well as food and beverage finished product distributors, traders, and manufacturers across Europe, USA, Canada, Australia, Thailand, Japan, Korea, Brazil, and Chile, among others.
ETprotein specialization includes exporting and delivering tailor-made protein powder and finished nutritional supplements. Their extensive product range covers sectors like Food and Beverage, Sports Nutrition, Weight Management, Dietary Supplements, Health and Wellness Products, and Infant Formula, ensuring comprehensive solutions to meet all your protein needs.
As a trusted company by leading global food and beverage brands and Fortune 500 companies, ETprotein reinforces China’s reputation in the global arena. For more information or to sample their products, please contact them and email sales(at)ETprotein.com today.












