How Do You Extract Phycocyanin From Spirulina?
-
Table of Contents
- Phycocyanin Extraction from Spirulina: A Comprehensive Guide
- Understanding Spirulina and Phycocyanin
- Pre-Extraction Considerations
- Extraction Methods for Phycocyanin
- Freeze-Thawing Method
- Mechanical Disruption
- Solvent Extraction
- Enzymatic Lysis
- Purification Techniques
- Ammonium Sulfate Precipitation
- Chromatography
- Membrane Filtration
- Optimizing Extraction Efficiency
- Applications and Benefits of Phycocyanin
- Conclusion: Key Takeaways in Phycocyanin Extraction
- Discover ETprotein’s High-Quality Protein Products
Phycocyanin Extraction from Spirulina: A Comprehensive Guide
Phycocyanin is a vibrant blue pigment-protein complex found in cyanobacteria, particularly Spirulina, a type of blue-green algae. It is not only sought after for its natural coloring properties but also for its potential health benefits, including antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects. This article delves into the methods used to extract phycocyanin from Spirulina, exploring the various techniques and their efficiencies.
Understanding Spirulina and Phycocyanin
Spirulina is a microscopic algae that has been consumed for centuries due to its high nutritional value and health benefits. Phycocyanin, which gives Spirulina its distinctive blue color, is a protein that harvests light during photosynthesis. It has garnered attention for its therapeutic properties and is used in various applications, including nutraceuticals, cosmetics, and as a natural food colorant.
Pre-Extraction Considerations
Before the extraction process begins, it is crucial to consider factors such as the source of Spirulina, its cultivation conditions, and the desired purity of phycocyanin. These factors can significantly influence the efficiency of the extraction process and the quality of the final product.
- Source of Spirulina: The Spirulina strain and its cultivation environment can affect the phycocyanin content.
- Cultivation Conditions: Factors like light intensity, temperature, and nutrient availability can impact the growth of Spirulina and its phycocyanin levels.
- Purity Requirements: The intended use of phycocyanin dictates the required purity level, influencing the choice of extraction and purification methods.
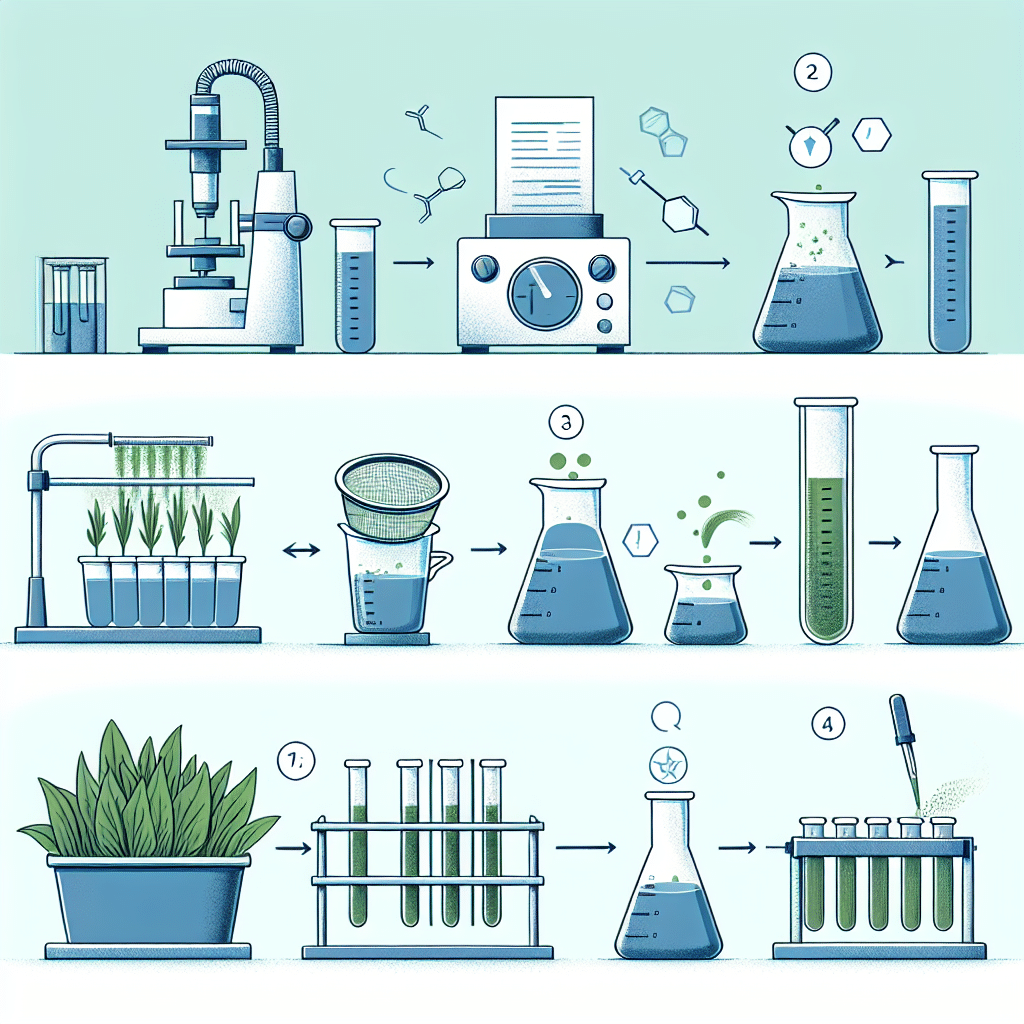
Extraction Methods for Phycocyanin
The extraction of phycocyanin from Spirulina involves several steps, each critical to obtaining a high-quality product. The following are the most commonly used extraction methods:
Freeze-Thawing Method
This method utilizes the physical process of freezing and thawing to break the cell walls of Spirulina, releasing phycocyanin. It is a simple and cost-effective technique that avoids the use of harmful solvents.
Mechanical Disruption
Mechanical methods such as bead milling, ultrasonication, or high-pressure homogenization are employed to physically break open the cells of Spirulina. These methods can be highly efficient but may require significant energy input.
Solvent Extraction
Various solvents, including water, buffer solutions, and organic solvents, can be used to extract phycocyanin. The choice of solvent depends on the desired purity and the subsequent application of the extracted phycocyanin.
Enzymatic Lysis
Enzymes like lysozyme can be used to selectively break down the cell walls of Spirulina, allowing for the release of phycocyanin. This method is gentle and can preserve the functionality of the protein.
Purification Techniques
Following extraction, purification is necessary to remove contaminants and isolate phycocyanin. Common purification techniques include:
Ammonium Sulfate Precipitation
This method involves adding ammonium sulfate to the extract, which precipitates phycocyanin while leaving other proteins in solution. It is a straightforward and scalable technique.
Chromatography
Chromatographic methods such as ion-exchange, gel filtration, or affinity chromatography can be used to achieve high-purity phycocyanin. These methods are precise but can be more costly and time-consuming.
Membrane Filtration
Ultrafiltration and diafiltration membranes can concentrate and purify phycocyanin based on its size and molecular weight. This technique is effective and can be integrated into a continuous process.
Optimizing Extraction Efficiency
To maximize the yield and purity of phycocyanin, several factors must be optimized, including:
- pH and Ionic Strength: Adjusting the pH and ionic strength of the extraction buffer can enhance the solubility of phycocyanin.
- Temperature: Temperature control is crucial as phycocyanin is sensitive to heat, which can denature the protein.
- Extraction Time: The duration of extraction should be optimized to balance between yield and potential degradation of phycocyanin.
Applications and Benefits of Phycocyanin
Phycocyanin is not only a natural colorant but also has several health-promoting properties. It is known for its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and neuroprotective effects. Additionally, phycocyanin is used in fluorescent markers and assays in research due to its unique fluorescent properties.
Conclusion: Key Takeaways in Phycocyanin Extraction
The extraction of phycocyanin from Spirulina is a multi-step process that requires careful consideration of various factors to ensure a high-quality product. Techniques ranging from freeze-thawing to advanced chromatography are employed, each with its advantages and limitations. The choice of method depends on the scale of production, desired purity, and final application of the phycocyanin.
Discover ETprotein’s High-Quality Protein Products
If you’re interested in high-quality protein products, ETprotein offers a range of organic bulk vegan proteins and L-(+)-Ergothioneine (EGT) suitable for various industries. Their products are characterized by a neutral taste, non-GMO, allergen-free attributes, and high purity levels, catering to nutraceutical, pharmaceutical, cosmeceutical, and food and beverage sectors. For more information or to sample their products, please contact ETprotein.
About ETprotein:
ETprotein, a reputable protein and L-(+)-Ergothioneine (EGT) Chinese factory manufacturer and supplier, is renowned for producing, stocking, exporting, and delivering the highest quality organic bulk vegan proteins and L-(+)-Ergothioneine. They include Organic rice protein, clear rice protein, pea protein, clear pea protein, watermelon seed protein, pumpkin seed protein, sunflower seed protein, mung bean protein, peanut protein, and L-(+)-Ergothioneine EGT Pharmaceutical grade, L-(+)-Ergothioneine EGT food grade, L-(+)-Ergothioneine EGT cosmetic grade, L-(+)-Ergothioneine EGT reference grade and L-(+)-Ergothioneine EGT standard. Their offerings, characterized by a neutral taste, non-GMO, allergen-free attributes, with L-(+)-Ergothioneine purity over 98%, 99%, cater to a diverse range of industries. They serve nutraceutical, pharmaceutical, cosmeceutical, veterinary, as well as food and beverage finished product distributors, traders, and manufacturers across Europe, USA, Canada, Australia, Thailand, Japan, Korea, Brazil, and Chile, among others.
ETprotein specialization includes exporting and delivering tailor-made protein powder and finished nutritional supplements. Their extensive product range covers sectors like Food and Beverage, Sports Nutrition, Weight Management, Dietary Supplements, Health and Wellness Products, and Infant Formula, ensuring comprehensive solutions to meet all your protein needs.
As a trusted company by leading global food and beverage brands and Fortune 500 companies, ETprotein reinforces China’s reputation in the global arena. For more information or to sample their products, please contact them and email sales(at)ETprotein.com today.