How Do You Extract Protein From Your Body?
-
Table of Contents
- Protein Extraction from the Body: Methods and Applications
- Understanding Protein Extraction
- Methods of Protein Extraction
- Applications of Extracted Proteins
- Challenges in Protein Extraction
- Case Studies and Statistics
- Conclusion: The Importance of Protein Extraction
- Discover ETprotein’s High-Quality Protein Products
Protein Extraction from the Body: Methods and Applications
Proteins are the building blocks of life, playing a crucial role in virtually every biological process. In the human body, they are essential for the structure, function, and regulation of tissues and organs. Understanding how to extract proteins from the body can be vital for various applications, including medical research, diagnostics, and therapeutic treatments. This article delves into the methods of protein extraction from the human body, their significance, and the potential applications of these proteins once isolated.
Understanding Protein Extraction
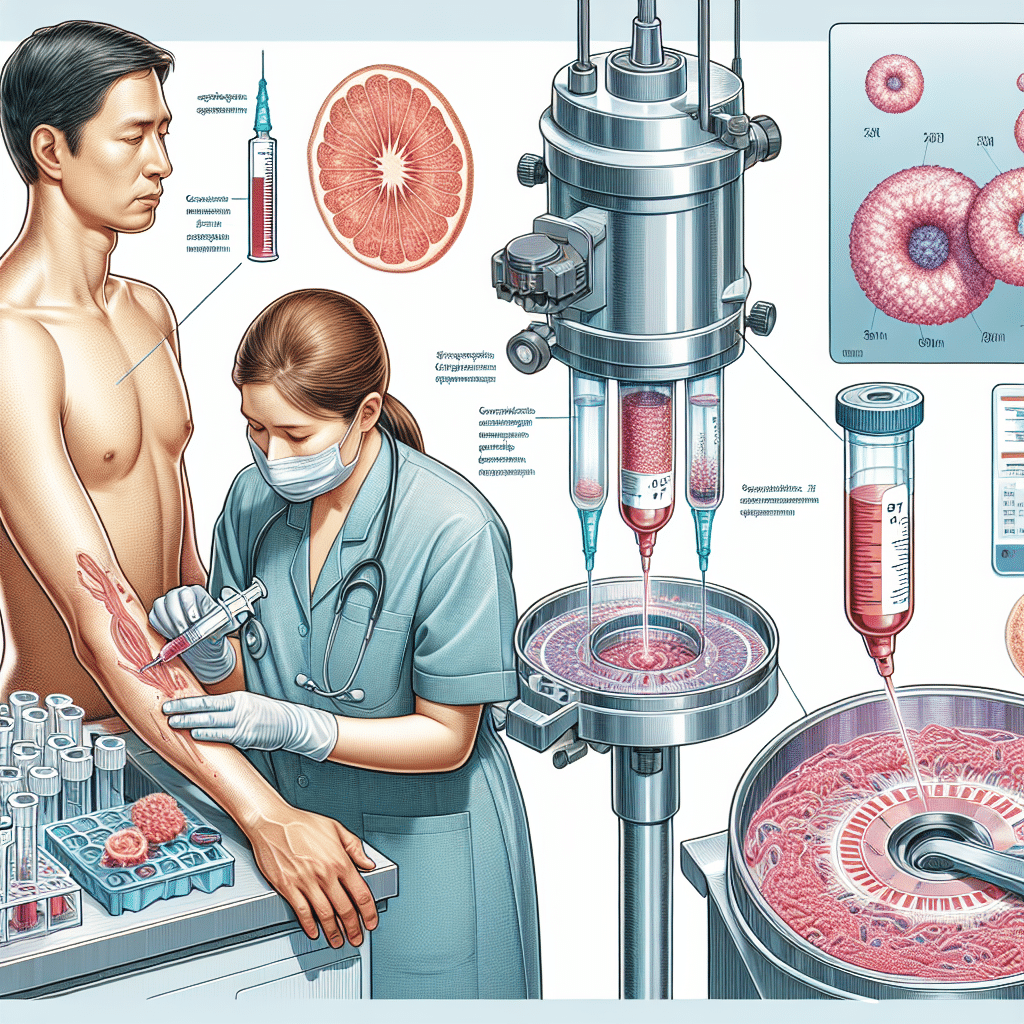
Protein extraction is the process of isolating proteins from biological samples. This can be done from tissues, cells, or bodily fluids. The purpose of protein extraction is to obtain a protein sample that is as pure as possible, free from other cellular components or contaminants that could interfere with further analysis or applications.
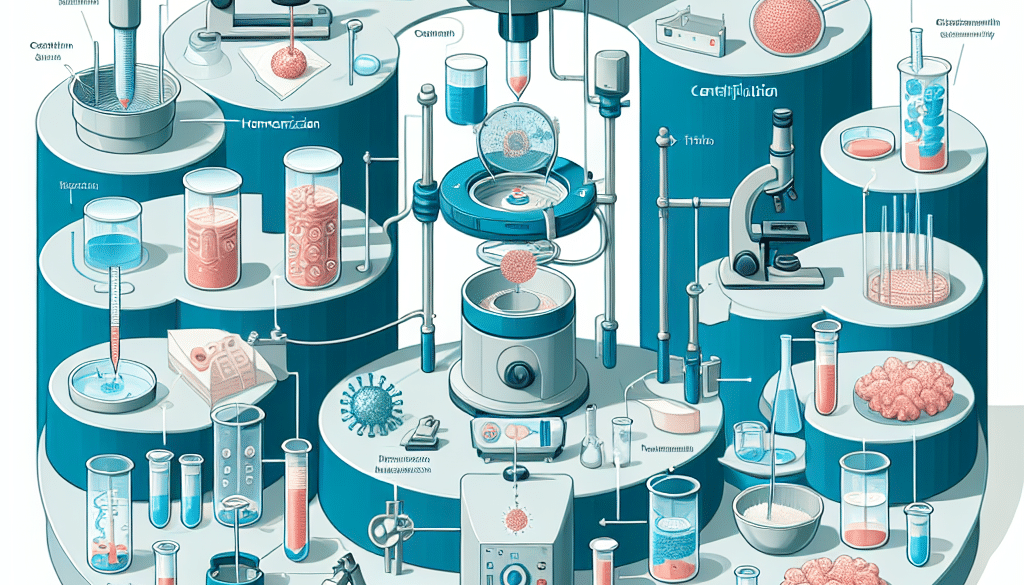
Methods of Protein Extraction
There are several methods used to extract proteins from the body, each with its own set of protocols and purposes. Here are some of the most common techniques:
- Cell Lysis: This method involves breaking open cells to release their contents, including proteins. Various techniques can be used for lysis, such as mechanical disruption, sonication, or the use of detergents.
- Centrifugation: After cell lysis, centrifugation is often used to separate proteins from other cell debris based on their size and density.
- Chromatography: This technique separates proteins based on their physical and chemical properties, such as size, charge, and hydrophobicity.
- Electrophoresis: Proteins can be separated by applying an electric field, which moves proteins through a gel matrix based on their size and charge.
- Immunoprecipitation: This method uses antibodies to selectively isolate specific proteins from a mixture.
Applications of Extracted Proteins
Once proteins are extracted, they can be used for a variety of applications:
- Biomedical Research: Studying the structure and function of proteins can lead to a better understanding of diseases and the development of new treatments.
- Diagnostics: Proteins can serve as biomarkers for various diseases, and their detection can aid in diagnosis.
- Therapeutics: Some proteins have therapeutic properties and can be used as drugs or in drug development.
Challenges in Protein Extraction
Protein extraction is not without its challenges. The complexity of the sample, the presence of proteases that can degrade proteins, and the need for maintaining protein stability are all factors that must be considered. Additionally, different proteins may require different extraction methods, making the process highly specialized.
Case Studies and Statistics
Several case studies have highlighted the importance of protein extraction in advancing medical science. For example, the extraction of specific proteins from cancer cells has led to the development of targeted cancer therapies. Statistics show that the global market for protein purification and isolation is growing, reflecting the increasing demand for pure proteins in research and therapeutics.
Conclusion: The Importance of Protein Extraction
In conclusion, protein extraction from the body is a critical process with wide-ranging applications in research, diagnostics, and therapeutics. The methods used to extract proteins are diverse and must be carefully chosen based on the specific protein and its intended use. Despite the challenges, the field of protein extraction continues to evolve, offering new possibilities for medical science and patient care.
Discover ETprotein’s High-Quality Protein Products
If you’re looking for premium protein products, ETprotein offers a range of organic bulk vegan proteins and L-(+)-Ergothioneine (EGT) suitable for various industries. Their products are characterized by a neutral taste, non-GMO, allergen-free attributes, and high purity levels, making them an excellent choice for your protein needs.
About ETprotein:
ETprotein, a reputable protein and L-(+)-Ergothioneine (EGT) Chinese factory manufacturer and supplier, is renowned for producing, stocking, exporting, and delivering the highest quality organic bulk vegan proteins and L-(+)-Ergothioneine. They include Organic rice protein, clear rice protein, pea protein, clear pea protein, watermelon seed protein, pumpkin seed protein, sunflower seed protein, mung bean protein, peanut protein, and L-(+)-Ergothioneine EGT Pharmaceutical grade, L-(+)-Ergothioneine EGT food grade, L-(+)-Ergothioneine EGT cosmetic grade, L-(+)-Ergothioneine EGT reference grade and L-(+)-Ergothioneine EGT standard. Their offerings, characterized by a neutral taste, non-GMO, allergen-free attributes, with L-(+)-Ergothioneine purity over 98%, 99%, cater to a diverse range of industries. They serve nutraceutical, pharmaceutical, cosmeceutical, veterinary, as well as food and beverage finished product distributors, traders, and manufacturers across Europe, USA, Canada, Australia, Thailand, Japan, Korea, Brazil, and Chile, among others.
ETprotein specialization includes exporting and delivering tailor-made protein powder and finished nutritional supplements. Their extensive product range covers sectors like Food and Beverage, Sports Nutrition, Weight Management, Dietary Supplements, Health and Wellness Products, and Infant Formula, ensuring comprehensive solutions to meet all your protein needs.
As a trusted company by leading global food and beverage brands and Fortune 500 companies, ETprotein reinforces China’s reputation in the global arena. For more information or to sample their products, please contact them and email sales(at)ETprotein.com today.