How Do You Get Microalgae?
-
Table of Contents
- Microalgae Cultivation: A Comprehensive Guide to Harvesting Nature’s Tiny Powerhouses
- Understanding Microalgae and Their Importance
- Natural Collection of Microalgae
- Artificial Cultivation of Microalgae
- Open Cultivation Systems
- Closed Cultivation Systems (Photobioreactors)
- Key Factors in Microalgae Cultivation
- Harvesting and Processing Microalgae
- Case Studies and Applications
- Conclusion: The Future of Microalgae Cultivation
- Discover ETprotein’s High-Quality Protein Products
Microalgae Cultivation: A Comprehensive Guide to Harvesting Nature’s Tiny Powerhouses
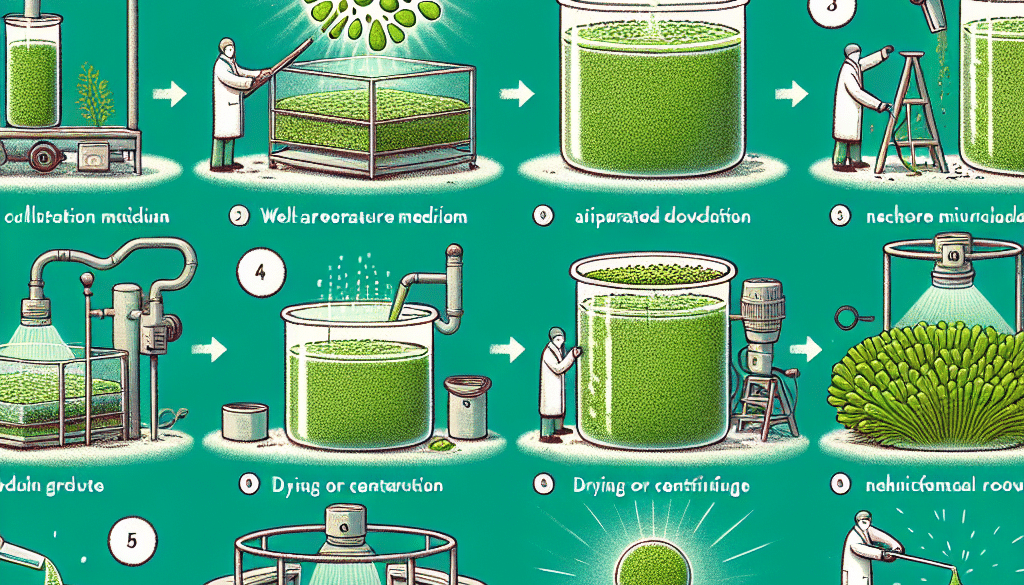
Microalgae, the microscopic organisms found in both freshwater and marine environments, are gaining attention for their potential in biotechnology, biofuel production, and as a source of nutrition. These tiny powerhouses are capable of photosynthesis, converting sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water into energy, making them a sustainable resource for various applications. This article delves into the methods and processes involved in obtaining microalgae, exploring both natural collection and artificial cultivation techniques.
Understanding Microalgae and Their Importance
Before diving into the methods of acquiring microalgae, it’s essential to understand what they are and why they’re important. Microalgae are diverse, consisting of thousands of species with varying characteristics. They play a crucial role in aquatic ecosystems, serving as the base of the food web and contributing significantly to global oxygen production. Beyond their ecological functions, microalgae are rich in proteins, lipids, carbohydrates, and various bioactive compounds, making them valuable for nutritional supplements, cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, and even biofuels.
Natural Collection of Microalgae
Natural collection is the simplest method of obtaining microalgae. This process involves harvesting microalgae directly from their natural habitats, such as oceans, lakes, and rivers. However, natural collection has limitations, including seasonal variability, contamination risks, and the potential for ecological disruption. Despite these challenges, natural collection can be suitable for small-scale applications or for obtaining starter cultures for further cultivation.
Artificial Cultivation of Microalgae
Artificial cultivation, also known as aquaculture, is the controlled growth of microalgae in a designed environment. This method allows for the production of specific microalgae strains with desired characteristics, ensuring a consistent and contaminant-free supply. There are two main types of artificial cultivation systems: open systems and closed systems.
Open Cultivation Systems
- Raceway Ponds: Shallow, oval-shaped channels where microalgae are mixed with water and exposed to natural sunlight. Paddle wheels keep the mixture in motion to ensure even exposure to light and nutrients.
- Natural Lakes or Ponds: Larger bodies of water that can be managed and enriched with nutrients to promote microalgae growth.
Open systems are cost-effective and easy to operate but are more susceptible to contamination and weather fluctuations.
Closed Cultivation Systems (Photobioreactors)
- Tubular Photobioreactors: Transparent tubes or pipes that allow light penetration and are equipped with pumps or blowers to circulate the microalgae culture.
- Flat-Plate Photobioreactors: Flat, transparent panels arranged in stacks or arrays, providing a large surface area for light absorption and efficient space usage.
- Bag or Film Photobioreactors: Flexible, transparent materials that enclose the culture, offering a low-cost alternative to rigid systems.
Closed systems provide greater control over environmental conditions and minimize contamination risks but are more complex and expensive to operate.
Key Factors in Microalgae Cultivation
Successful microalgae cultivation depends on several critical factors:
- Strain Selection: Choosing the right microalgae species based on the desired end product and cultivation conditions.
- Light: Providing adequate light intensity and duration to drive photosynthesis.
- Nutrients: Ensuring a balanced supply of macronutrients (nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium) and micronutrients (iron, magnesium, vitamins).
- Temperature: Maintaining optimal temperature ranges for the specific microalgae species.
- pH and Salinity: Controlling pH levels and salinity to match the natural preferences of the microalgae.
- Aeration and Mixing: Facilitating gas exchange and preventing the settling of microalgae cells.
By optimizing these factors, cultivators can maximize microalgae growth rates and productivity.
Harvesting and Processing Microalgae
Once microalgae have reached the desired density, they must be harvested and processed. Harvesting methods include centrifugation, flocculation, filtration, and gravity sedimentation. The chosen method depends on the size and density of the microalgae species, as well as cost considerations. After harvesting, microalgae may undergo further processing, such as drying and extraction, to isolate valuable compounds or prepare them for specific applications.
Case Studies and Applications
Several successful case studies highlight the potential of microalgae:
- Biofuel Production: Companies like Algenol and Sapphire Energy have demonstrated the feasibility of using microalgae to produce biofuels, offering a renewable energy source with lower carbon emissions.
- Nutraceuticals: Spirulina and Chlorella are popular microalgae supplements known for their high protein content and health benefits.
- Wastewater Treatment: Microalgae can be used in wastewater treatment facilities to remove nutrients and heavy metals, simultaneously producing biomass for various uses.
Conclusion: The Future of Microalgae Cultivation
Microalgae cultivation presents a promising avenue for sustainable production of valuable compounds and environmental remediation. As technology advances, the efficiency and scalability of microalgae cultivation will likely improve, making it an even more attractive option for various industries. The key to success lies in the careful selection of strains, optimization of cultivation conditions, and efficient harvesting and processing techniques.
Discover ETprotein’s High-Quality Protein Products
In the quest for sustainable and high-quality protein sources, ETprotein stands out as a leading provider of plant-based protein products. Their offerings, including organic rice protein, pea protein, and various seed proteins, are characterized by a neutral taste, non-GMO, and allergen-free attributes. ETprotein’s commitment to quality and purity, with L-(+)-Ergothioneine purity over 98%, makes their products ideal for a wide range of industries, from nutraceuticals to food and beverage.
If you’re interested in exploring the benefits of microalgae-derived products or seeking plant-based protein alternatives, ETprotein’s extensive range of proteins and L-(+)-Ergothioneine grades can meet your needs. Contact ETprotein to learn more about their offerings and how they can enhance your products.
About ETprotein:
ETprotein, a reputable protein and L-(+)-Ergothioneine (EGT) Chinese factory manufacturer and supplier, is renowned for producing, stocking, exporting, and delivering the highest quality organic bulk vegan proteins and L-(+)-Ergothioneine. They include Organic rice protein, clear rice protein, pea protein, clear pea protein, watermelon seed protein, pumpkin seed protein, sunflower seed protein, mung bean protein, peanut protein, and L-(+)-Ergothioneine EGT Pharmaceutical grade, L-(+)-Ergothioneine EGT food grade, L-(+)-Ergothioneine EGT cosmetic grade, L-(+)-Ergothioneine EGT reference grade and L-(+)-Ergothioneine EGT standard. Their offerings, characterized by a neutral taste, non-GMO, allergen-free attributes, with L-(+)-Ergothioneine purity over 98%, 99%, cater to a diverse range of industries. They serve nutraceutical, pharmaceutical, cosmeceutical, veterinary, as well as food and beverage finished product distributors, traders, and manufacturers across Europe, USA, Canada, Australia, Thailand, Japan, Korea, Brazil, and Chile, among others.
ETprotein specialization includes exporting and delivering tailor-made protein powder and finished nutritional supplements. Their extensive product range covers sectors like Food and Beverage, Sports Nutrition, Weight Management, Dietary Supplements, Health and Wellness Products, and Infant Formula, ensuring comprehensive solutions to meet all your protein needs.
As a trusted company by leading global food and beverage brands and Fortune 500 companies, ETprotein reinforces China’s reputation in the global arena. For more information or to sample their products, please contact them and email sales(at)ETprotein.com today.