Is a Watermelon a Fruit? The Surprising Answer”
-
Table of Contents
- Watermelon Wonders: Is It a Fruit or Something More?
- Botanical Background: The Fruit or Vegetable Debate
- Watermelon’s Surprising Relatives
- Historical and Cultural Perspectives
- Nutritional Profile of Watermelon
- Watermelon in Research and Case Studies
- Conclusion: Embracing the Duality of Watermelon
- Discover the Power of Watermelon Seed Protein with ETprotein
Watermelon Wonders: Is It a Fruit or Something More?
Watermelon is a staple of summer picnics and beach outings, known for its refreshing juiciness and sweet taste. But have you ever stopped to ponder whether this green-skinned delight is a fruit, a vegetable, or something else entirely? The answer might surprise you. In this article, we’ll delve into the botanical and culinary classifications of watermelon, explore its origins, and discuss its nutritional benefits. By the end, you’ll have a newfound appreciation for this fascinating food.
Botanical Background: The Fruit or Vegetable Debate
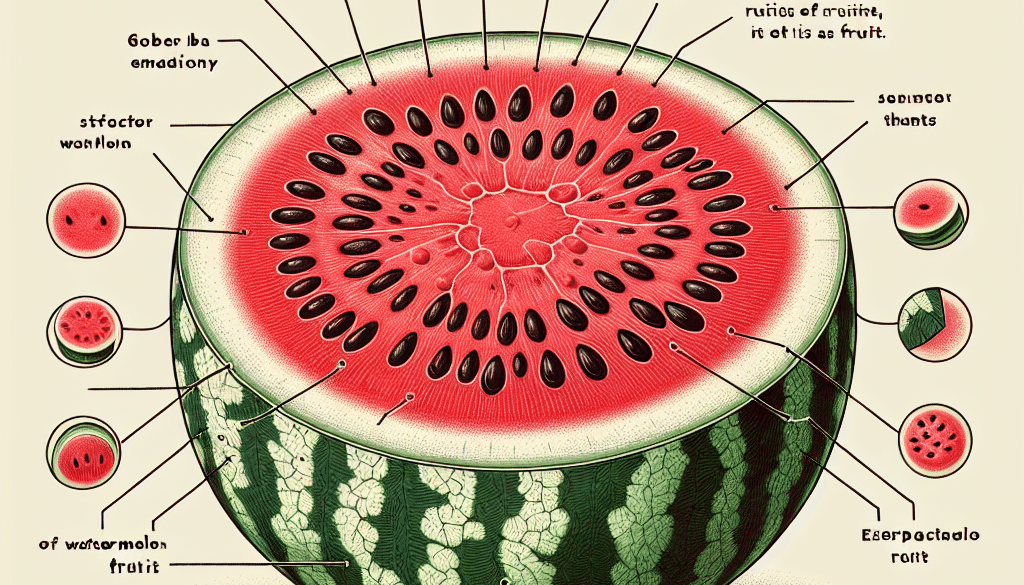
From a botanical standpoint, the classification of watermelon is quite clear. Botanically, a fruit is the mature ovary of a flowering plant, usually containing seeds. By this definition, watermelon qualifies as a fruit. More specifically, it is considered a pepo—a type of berry with a thick rind and fleshy center, which is characteristic of the Cucurbitaceae family that includes cucumbers, pumpkins, and squash.
However, the story doesn’t end there. In the culinary world, the distinction between fruits and vegetables is based on taste and usage. Fruits are typically sweet and used in desserts, while vegetables are more savory and used in main dishes. Because watermelon is sweet and commonly consumed as a dessert or snack, it is generally classified as a fruit in the culinary context.
Watermelon’s Surprising Relatives
Interestingly, watermelon’s family ties might cause some to reconsider its classification. As a member of the Cucurbitaceae family, watermelon is closely related to vegetables like cucumbers, pumpkins, and gourds. In some cultures, watermelon is even prepared and eaten as a vegetable. For example, in China, the rind is stir-fried, stewed, or pickled, which is a practice that might lead some to view watermelon as more vegetable than fruit.
Historical and Cultural Perspectives
The history of watermelon can shed light on its classification. Watermelon has been cultivated for thousands of years, with evidence of its consumption dating back to Ancient Egypt. It was not only eaten but also used to store water for long journeys across the desert. This utilitarian use might suggest a classification more akin to a vegetable, which historically has been associated with sustenance and survival.
Nutritional Profile of Watermelon
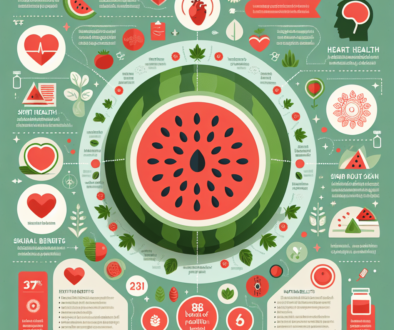
Regardless of its classification, watermelon is a nutritional powerhouse. It is low in calories but rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. Here are some of the key nutritional benefits of watermelon:
- Hydration: Watermelon is approximately 92% water, making it an excellent choice for staying hydrated.
- Vitamin C: A serving of watermelon provides a significant amount of vitamin C, which is important for immune function and skin health.
- Lycopene: This antioxidant gives watermelon its red color and is linked to heart health and cancer prevention.
- Amino acids: Watermelon contains citrulline, an amino acid that may improve blood flow and reduce muscle soreness.
With its combination of hydration and nutrition, watermelon is a great addition to any diet.
Watermelon in Research and Case Studies
Scientific research has supported the health benefits of watermelon. For instance, studies have shown that lycopene intake is associated with a lower risk of certain types of cancer. Additionally, watermelon’s high water content and natural sugars can provide athletes with a quick source of energy and hydration during intense physical activity.
In one case study, athletes who consumed watermelon juice before an intense workout reported less muscle soreness and a faster heart rate recovery compared to those who did not. This suggests that watermelon can be an effective food for sports nutrition.
Conclusion: Embracing the Duality of Watermelon
In conclusion, watermelon is both a fruit and a vegetable, depending on the perspective you choose. Botanically, it is a fruit—a berry, to be precise. Culinary practices often treat it as a fruit due to its sweet flavor. Yet, its versatility and relation to other vegetables mean that it can cross categories. What’s most important is that watermelon is a nutritious and hydrating food that can be enjoyed in a variety of ways.
Whether you consider watermelon a fruit or a vegetable, one thing is certain: it is a delightful addition to any meal or snack, offering a wealth of health benefits. So next time you bite into a juicy slice of watermelon, remember the surprising complexity behind this summer favorite.
Discover the Power of Watermelon Seed Protein with ETprotein
If you’re intrigued by the nutritional benefits of watermelon, you’ll be excited to learn about ETprotein’s watermelon seed protein products. Watermelon seeds are a fantastic source of plant-based protein and can be a great addition to your diet, especially if you’re looking for vegan protein options.
ETprotein is a leading watermelon seed protein Chinese factory manufacturer and supplier, offering a range of high-quality organic bulk vegan protein and plant proteins. Their watermelon seed protein is characterized by a neutral taste, non-GMO, and allergen-free attributes, making it suitable for a wide array of applications in the food and beverage industry.
Whether you’re a distributor, trader, or manufacturer, ETprotein can provide you with the protein solutions you need. Their commitment to quality and customer service has made them a trusted partner for global food and beverage brands and Fortune 500 companies. To learn more about their products or to request a sample, contact ETprotein today.
About ETprotein:
ETprotein, a reputable watermelon seed protein Chinese factory manufacturer and supplier, is renowned for producing, stocking, exporting, and delivering the highest quality organic bulk vegan protein and plant proteins. They include Organic rice protein, clear rice protein, pea protein, clear pea protein, watermelon seed protein, pumpkin seed protein, sunflower seed protein, mung bean protein, peanut protein etc. Their offerings, characterized by a neutral taste, non-GMO, allergen-free attributes, cater to a diverse range of industries. They serve nutraceutical, pharmaceutical, cosmeceutical, veterinary, as well as food and beverage finished product distributors, traders, and manufacturers across Europe, USA, Canada, Australia, Thailand, Japan, Korea, Brazil, and Chile, among others.
ETprotein specialization includes exporting and delivering tailor-made protein powder and finished nutritional supplements. Their extensive product range covers sectors like Food and Beverage, Sports Nutrition, Weight Management, Dietary Supplements, Health and Wellness Products, and Infant Formula, ensuring comprehensive solutions to meet all your protein needs.
As a trusted company by leading global food and beverage brands and Fortune 500 companies, ETprotein reinforces China’s reputation in the global arena. For more information or to sample their products, please contact them and email sales(at)ETprotein.com today.