Is Watermelon a Fruit? Clearing Up Confusion
-
Table of Contents
- Watermelon: Fruit or Vegetable? Understanding the Classification
- Botanical Perspective: Watermelon as a Fruit
- Culinary Uses: Watermelon in the Kitchen
- Nutritional Profile: Health Benefits of Watermelon
- Case Studies and Research
- Conclusion: Embracing Watermelon in All Its Forms
- Discover the Power of Watermelon Seed Protein with ETprotein
Watermelon: Fruit or Vegetable? Understanding the Classification

Watermelon is a staple of summer picnics and beach outings, known for its refreshing juiciness and sweet taste. However, there’s a common question that often arises in discussions about this popular produce: Is watermelon a fruit? This article aims to clear up any confusion surrounding the classification of watermelon, delving into botanical definitions, culinary uses, and nutritional benefits. By exploring scientific evidence and expert opinions, we’ll provide a comprehensive understanding of where watermelon fits in the world of plant-based foods.
Botanical Perspective: Watermelon as a Fruit
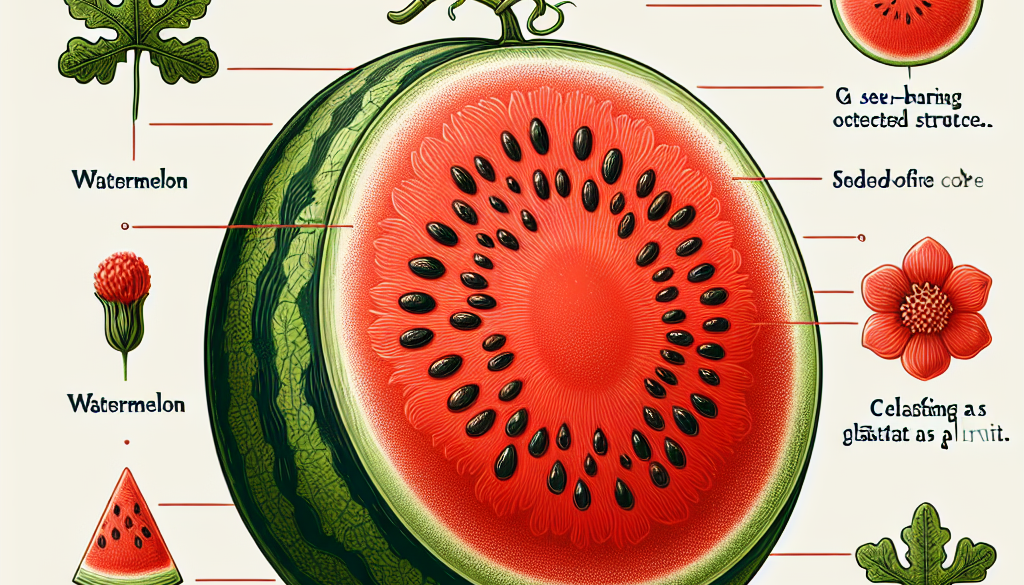
From a botanical standpoint, watermelon is unequivocally classified as a fruit. More specifically, it is considered a berry, known as a pepo. Botanists define fruit as the mature ovary of a flowering plant, usually containing seeds. Fruits develop from the fertilized ovules of flowers and serve as a mechanism for seed dispersal. Watermelon fits this definition perfectly, as it grows from the flower of the watermelon plant (Citrullus lanatus) and contains numerous seeds that can give rise to new plants.
- Anatomy of Watermelon: The watermelon fruit is composed of a thick rind, a fleshy center (mesocarp and endocarp), and seeds.
- Reproductive Role: Watermelons play a crucial role in the plant’s reproductive cycle by housing and protecting the seeds until they are ready to be dispersed.
- Classification as a Berry: In botanical terms, a berry is a simple fruit with seeds and pulp produced from the ovary of a single flower. The rind of the watermelon is the exocarp, the middle juicy part is the mesocarp, and the part surrounding the seed is the endocarp.
Culinary Uses: Watermelon in the Kitchen
In the culinary world, the distinction between fruits and vegetables is less clear-cut and often based on taste and tradition rather than scientific criteria. Fruits are typically sweet or tart and used in desserts, snacks, or beverages, while vegetables are more savory and used in main dishes or sides. Watermelon, with its sweet flavor profile, is generally treated as a fruit in the kitchen. It is commonly consumed fresh in fruit salads, as juice, or as a refreshing snack. However, in some cultures, watermelon is also used in savory dishes, which can blur the lines of its classification.
- Desserts and Beverages: Watermelon is a popular ingredient in smoothies, popsicles, and fruit tarts.
- Savory Dishes: In some cuisines, watermelon rind is pickled or stir-fried, showcasing its versatility beyond sweet applications.
Nutritional Profile: Health Benefits of Watermelon
Watermelon is not only delicious but also packed with nutrients and health benefits. It is low in calories and high in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. Here’s a closer look at the nutritional value of watermelon:
- Hydration: Watermelon is composed of about 92% water, making it an excellent choice for staying hydrated, especially during hot weather.
- Vitamins and Minerals: It is a good source of vitamin C, vitamin A, potassium, and magnesium.
- Antioxidants: Watermelon contains compounds like lycopene and cucurbitacin E, which have antioxidant properties and may help reduce inflammation and oxidative damage.
Regular consumption of watermelon can contribute to a healthy diet, supporting cardiovascular health, boosting the immune system, and potentially reducing the risk of certain diseases.
Case Studies and Research
Several studies have investigated the health benefits of watermelon. For instance, research has shown that lycopene, the compound that gives watermelon its red color, may help lower the risk of heart disease and some types of cancer. Another study suggests that the amino acid citrulline, found in watermelon, may improve exercise performance and reduce muscle soreness.
- Cardiovascular Health: Lycopene has been linked to reduced blood pressure and lower risk of heart attacks.
- Cancer Prevention: Some studies suggest that lycopene may play a role in preventing prostate cancer.
- Exercise Performance: Citrulline may enhance athletic performance by improving blood flow and reducing fatigue.
Conclusion: Embracing Watermelon in All Its Forms
In conclusion, watermelon is scientifically classified as a fruit, specifically a type of berry known as a pepo. Its role in the plant’s reproductive process, along with its seed-bearing structure, aligns with the botanical definition of fruit. Culinary practices often reinforce this classification, as watermelon’s sweet taste makes it a favorite in fruit salads, desserts, and refreshing drinks. Beyond its delicious flavor, watermelon offers significant health benefits, including hydration, essential nutrients, and antioxidants that promote overall well-being.
Whether enjoyed as a juicy snack on a hot day or incorporated into both sweet and savory dishes, watermelon is a versatile and nutritious addition to any diet. Understanding its classification helps consumers appreciate the complexities of plant biology and the diverse roles that watermelon can play on our plates and in our health.
Discover the Power of Watermelon Seed Protein with ETprotein
While watermelon flesh gets most of the attention, its seeds are also a powerhouse of nutrition. ETprotein harnesses the benefits of these seeds by offering high-quality watermelon seed protein products. This plant-based protein is an excellent choice for those looking to incorporate more vegan protein options into their diet.
ETprotein’s watermelon seed protein is perfect for individuals with dietary restrictions, as it is non-GMO and allergen-free. It can be used in a variety of applications, from sports nutrition to health and wellness products. If you’re interested in exploring the nutritional advantages of watermelon seed protein or other plant proteins, consider ETprotein for your needs.
About ETprotein:
ETprotein, a reputable watermelon seed protein Chinese factory manufacturer and supplier, is renowned for producing, stocking, exporting, and delivering the highest quality organic bulk vegan protein and plant proteins. They include Organic rice protein, clear rice protein, pea protein, clear pea protein, watermelon seed protein, pumpkin seed protein, sunflower seed protein, mung bean protein, peanut protein etc. Their offerings, characterized by a neutral taste, non-GMO, allergen-free attributes, cater to a diverse range of industries. They serve nutraceutical, pharmaceutical, cosmeceutical, veterinary, as well as food and beverage finished product distributors, traders, and manufacturers across Europe, USA, Canada, Australia, Thailand, Japan, Korea, Brazil, and Chile, among others.
ETprotein specialization includes exporting and delivering tailor-made protein powder and finished nutritional supplements. Their extensive product range covers sectors like Food and Beverage, Sports Nutrition, Weight Management, Dietary Supplements, Health and Wellness Products, and Infant Formula, ensuring comprehensive solutions to meet all your protein needs.
As a trusted company by leading global food and beverage brands and Fortune 500 companies, ETprotein reinforces China’s reputation in the global arena. For more information or to sample their products, please contact them and email sales(at)ETprotein.com today.