Mung Bean Varietals: Exploring Diversity
-
Table of Contents
- Mung Bean Varietals: Unveiling the Rich Diversity and Benefits
- The Origins and Importance of Mung Beans
- Exploring the Spectrum of Mung Bean Varietals
- Nutritional Profile of Mung Beans
- Case Studies: Success Stories of Mung Bean Cultivation
- Global Mung Bean Production and Consumption Trends
- Culinary Uses of Mung Beans
- Challenges and Opportunities in Mung Bean Cultivation
- Conclusion: Embracing the Diversity of Mung Beans
- Discover ETprotein’s High-Quality Mung Bean Protein Products
Mung Bean Varietals: Unveiling the Rich Diversity and Benefits
Mung beans, a staple in many cuisines across the globe, are not only a source of rich nutrition but also a testament to agricultural diversity. With a history that spans thousands of years, these small, green legumes have been cultivated and cherished for their versatility in dishes and their health benefits. In this comprehensive exploration, we delve into the world of mung bean varietals, examining their unique characteristics, nutritional profiles, and the role they play in sustainable agriculture and global food security.
The Origins and Importance of Mung Beans
Mung beans (Vigna radiata) are believed to have originated in India and have spread throughout Asia, Africa, and the Americas. They are a key ingredient in many traditional dishes and are valued for their high protein content, dietary fiber, and low glycemic index. Mung beans are also environmentally friendly crops, requiring less water and fertilizers compared to other legumes, making them a sustainable choice for farmers and consumers alike.
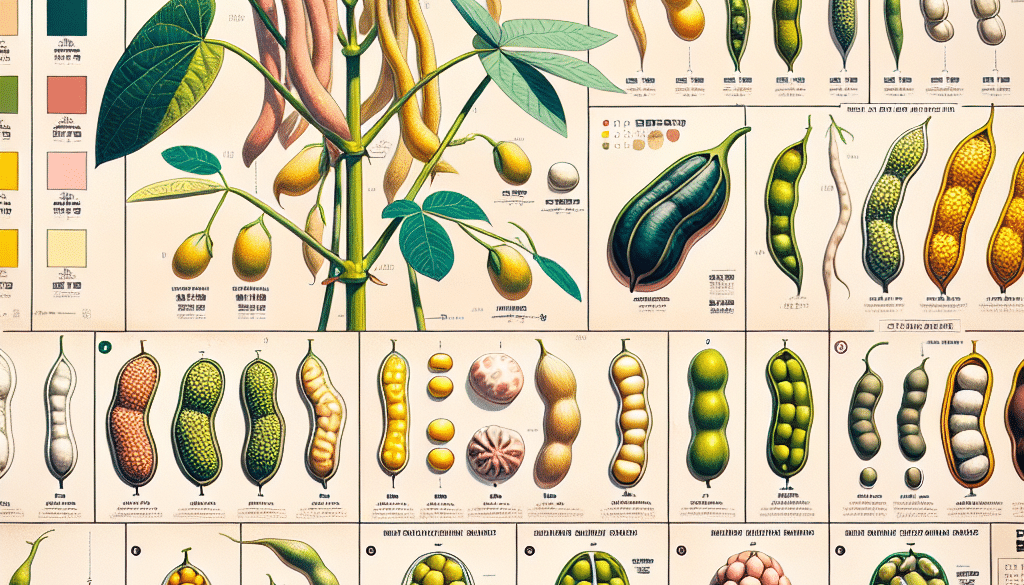
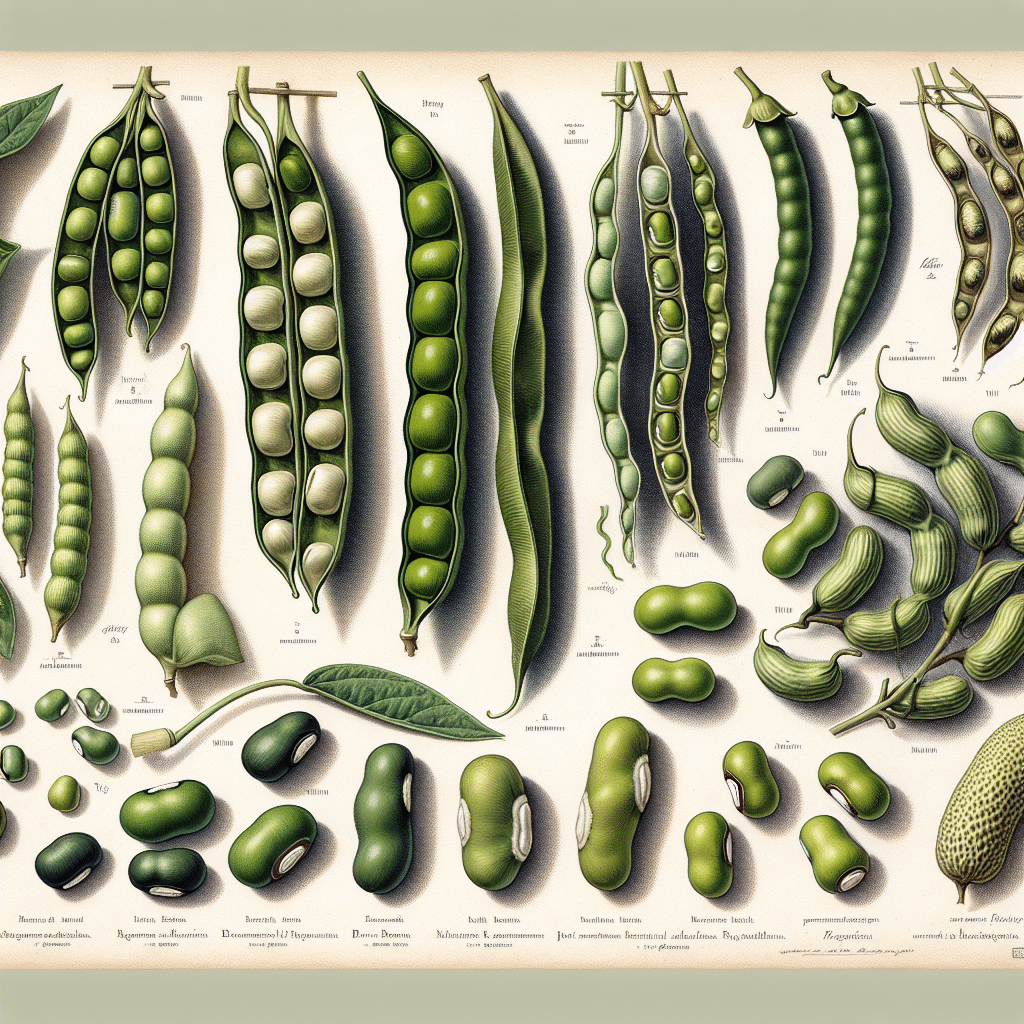
Exploring the Spectrum of Mung Bean Varietals
There is a surprising array of mung bean varietals, each with its own set of characteristics that cater to different climates, tastes, and uses. Here are some of the most notable varietals:
- Pusa Vishal – A variety known for its large seeds and high yield, popular in India.
- Pusa Ratna – Another Indian variety that is resistant to yellow mosaic virus and powdery mildew.
- Sukha – A drought-resistant variety from Myanmar, suitable for dry climates.
- KPS1 – A high-yielding variety from Kenya, known for its pest resistance.
- VIR372 – A Russian variety that is adapted to cooler climates and has a short growing season.
Each of these varietals has been developed to optimize yield, disease resistance, and adaptability to different environmental conditions, showcasing the genetic diversity within mung beans.
Nutritional Profile of Mung Beans
Mung beans are a nutritional powerhouse, offering a wealth of health benefits. They are rich in:
- Protein – Essential for muscle repair and growth.
- Dietary fiber – Aids in digestion and promotes a feeling of fullness.
- Vitamins – Including vitamin C, B vitamins, and vitamin K.
- Minerals – Such as potassium, magnesium, iron, and zinc.
- Antioxidants – Compounds that help combat oxidative stress in the body.
Their low glycemic index makes them an excellent food choice for managing blood sugar levels, and their high fiber content is beneficial for heart health.
Case Studies: Success Stories of Mung Bean Cultivation
Several case studies highlight the success of mung bean cultivation in various parts of the world:
- In India, the introduction of disease-resistant varietals has led to increased yields and farmer income.
- In Australia, research on mung bean adaptation to local climates has expanded their cultivation, making Australia a significant exporter of mung beans.
- In the United States, mung beans are being explored as a cover crop to improve soil health and reduce erosion.
These examples demonstrate the adaptability of mung beans and their potential to contribute to sustainable agriculture practices.
Global Mung Bean Production and Consumption Trends
Statistics show that global mung bean production has been steadily increasing to meet the rising demand for plant-based proteins and sustainable crops. Asia remains the largest producer and consumer of mung beans, with countries like India, China, and Myanmar leading the way. However, there is growing interest in mung beans in Western countries as consumers seek healthier and more diverse plant-based options.
Culinary Uses of Mung Beans
Mung beans are incredibly versatile in the kitchen. They can be used in a variety of dishes:
- Sprouted – Commonly used in salads, sandwiches, and stir-fries.
- Whole – Used in soups, stews, and as a side dish.
- Split – Used to make traditional dishes like dal in South Asian cuisine.
- Flour – Utilized in making noodles, pancakes, and desserts.
This versatility not only makes mung beans a culinary delight but also allows for their incorporation into various diets and meal plans.
Challenges and Opportunities in Mung Bean Cultivation
While mung beans offer many advantages, there are challenges that need to be addressed:
- Disease and pest management remain critical for maintaining healthy crops.
- Climate change poses a threat to traditional growing regions, necessitating the development of more resilient varietals.
- Market access and infrastructure improvements are needed to support smallholder farmers.
However, these challenges also present opportunities for innovation in breeding techniques, sustainable farming practices, and market development.
Conclusion: Embracing the Diversity of Mung Beans
The exploration of mung bean varietals reveals a world of diversity that has significant implications for nutrition, cuisine, and agriculture. By understanding and promoting this diversity, we can harness the full potential of mung beans to contribute to a more sustainable and health-conscious future. The key takeaways from this article emphasize the importance of continued research, breeding efforts, and support for farmers to ensure that mung beans remain a valuable resource for generations to come.
Discover ETprotein’s High-Quality Mung Bean Protein Products
In line with the growing interest in plant-based nutrition, ETprotein offers a range of high-quality mung bean protein products. Their mung bean protein is characterized by its neutral taste and non-GMO, allergen-free attributes, making it an excellent choice for various industries, including food and beverage, sports nutrition, and health and wellness products. By choosing ETprotein’s mung bean protein, consumers and manufacturers can benefit from a sustainable and nutritious plant protein source that supports a healthy lifestyle.
About ETprotein:
ETprotein, a reputable protein Chinese factory manufacturer and supplier, is renowned for producing, stocking, exporting, and delivering the highest quality organic bulk vegan protein and plant proteins. They include Organic rice protein, clear rice protein, pea protein, clear pea protein, pumpkin seed protein, sunflower seed protein, mung bean protein, etc. Their offerings, characterized by a neutral taste, non-GMO, allergen-free attributes, cater to a diverse range of industries. They serve nutraceutical, pharmaceutical, cosmeceutical, veterinary, as well as food and beverage finished product distributors, traders, and manufacturers across Europe, USA, Canada, Australia, Thailand, Japan, Korea, Brazil, and Chile, among others.
ETprotein specialization includes exporting and delivering tailor-made protein powder and finished nutritional supplements. Their extensive product range covers sectors like Food and Beverage, Sports Nutrition, Weight Management, Dietary Supplements, Health and Wellness Products, and Infant Formula, ensuring comprehensive solutions to meet all your protein needs.
As a trusted company by leading global food and beverage brands and Fortune 500 companies, ETprotein reinforces China’s reputation in the global arena. For more information or to sample their products, please contact them and email sales(at)ETprotein.com today.