Parts of Peanut: Unveiling The Nutty Details
-
Table of Contents
- Exploring the Nutty Details: A Deep Dive into Peanut Parts
- The Anatomy of a Peanut Plant
- Nutritional Profile of Peanuts
- Economic Impact and Uses of Peanuts
- Environmental Considerations
- Challenges in Peanut Production
- Conclusion: The Multifaceted World of Peanuts
- Discover ETprotein’s High-Quality Peanut Protein Products
Exploring the Nutty Details: A Deep Dive into Peanut Parts
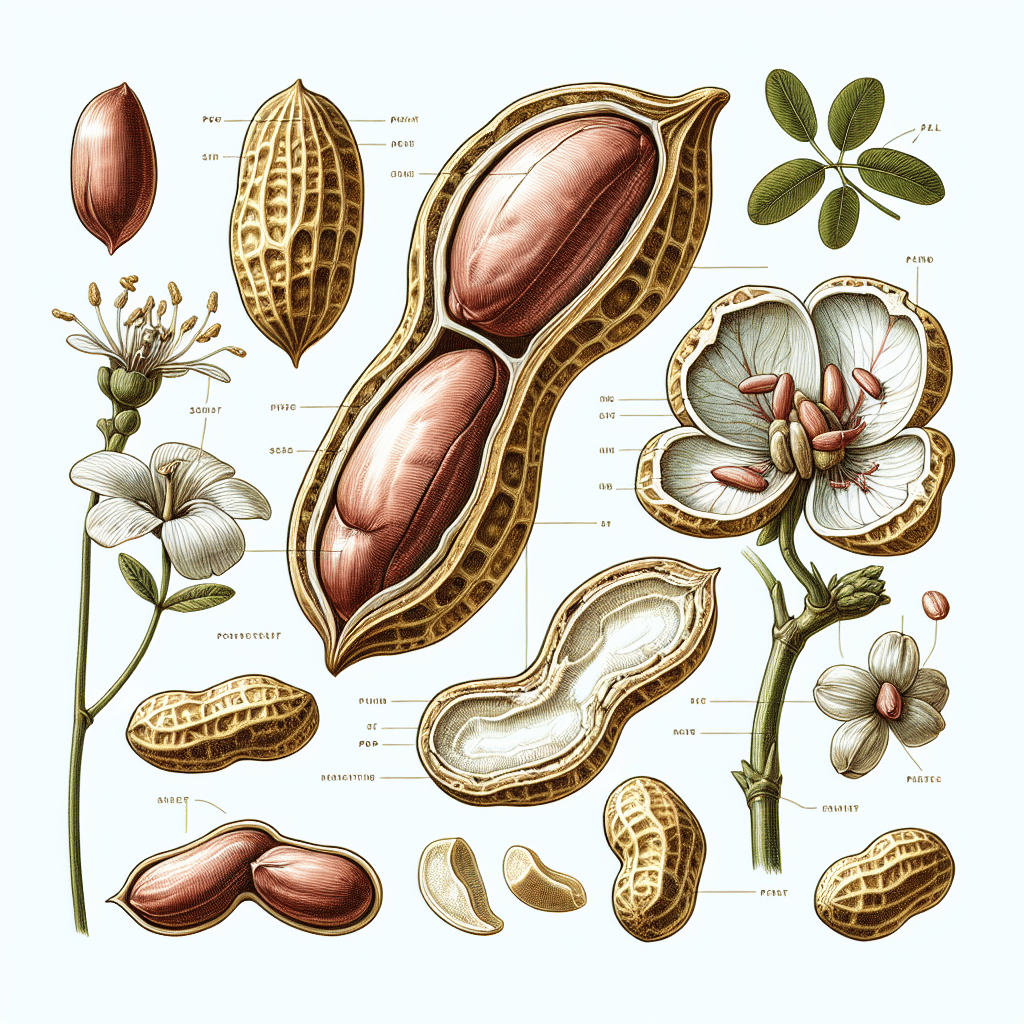
Peanuts, often mistaken for nuts, are actually legumes that have become a staple in diets around the world. They are not only a source of delicious snacks and ingredients but also play a significant role in various industries due to their nutritional value and versatility. In this article, we will explore the different parts of the peanut plant and their uses, nutritional benefits, and impact on the economy.
The Anatomy of a Peanut Plant
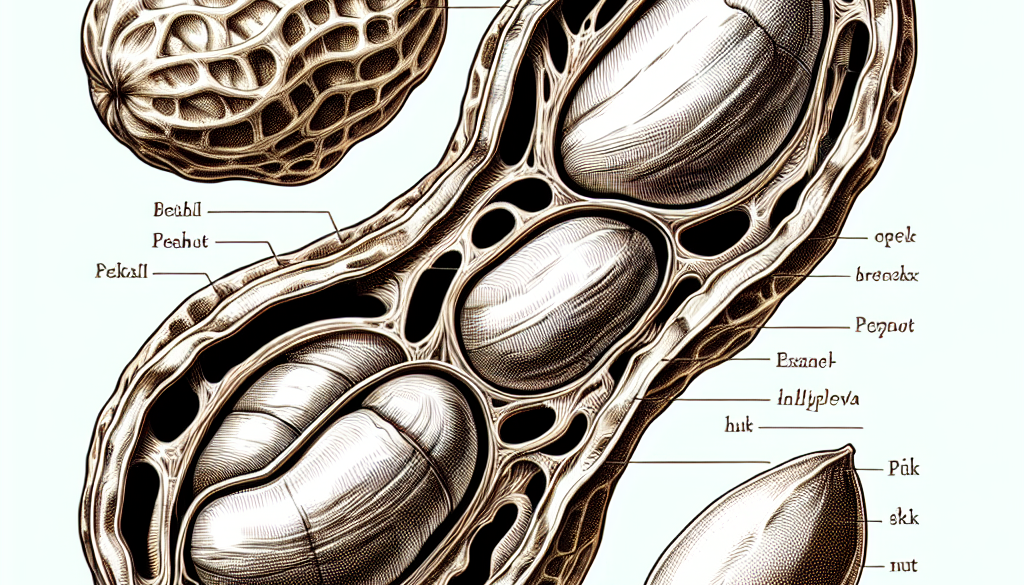
The peanut plant, scientifically known as Arachis hypogaea, is a fascinating specimen. It undergoes a unique process called geocarpy, where the flower pollinates above ground and then the fertilized ovary, known as a peg, extends down into the soil to mature into a peanut. Let’s break down the plant into its key components:
- The Shell: The outermost layer that encases the peanut kernels. It is fibrous and serves as protection during the development and maturation of the seeds.
- The Kernel: This is the edible part of the peanut, which is rich in oils, proteins, and other nutrients. It is often roasted and consumed directly or processed into various products.
- The Skin: A thin, papery layer that covers the kernel. It contains antioxidants and can be left on or removed during processing.
- The Root System: Peanuts have a strong root system that helps in fixing nitrogen in the soil, making them beneficial for crop rotation and soil health.
- The Leaves and Stems: While not directly consumed, they play a crucial role in photosynthesis and the overall growth of the plant.
Nutritional Profile of Peanuts
Peanuts are a powerhouse of nutrition, offering a range of health benefits. They are rich in monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats, which are good for heart health. Peanuts also contain essential vitamins and minerals such as Vitamin E, magnesium, and potassium. Furthermore, they are an excellent source of protein, making them a popular choice for vegetarians and vegans seeking to increase their protein intake.
Economic Impact and Uses of Peanuts
The peanut industry is a significant contributor to the economies of many countries. The United States, China, and India are among the top producers of peanuts. The legume is used in various forms, from peanut butter to oil, and even in the production of livestock feed. The versatility of peanuts extends to non-food uses as well, such as in the manufacture of biodiesel and as an ingredient in skincare products.
Environmental Considerations
Peanuts have a relatively low water footprint compared to other crops, making them an environmentally friendly option. Their ability to fix nitrogen in the soil reduces the need for chemical fertilizers, promoting sustainable farming practices. However, it is essential to manage peanut cultivation responsibly to prevent soil depletion and maintain biodiversity.
Challenges in Peanut Production
Despite their benefits, peanut cultivation faces challenges such as susceptibility to diseases and pests. Aflatoxin, a toxin produced by certain molds that can grow on peanuts, poses a significant health risk if not properly managed. Advances in agricultural technology and practices are continually being developed to address these issues and improve the safety and sustainability of peanut production.
Conclusion: The Multifaceted World of Peanuts
In conclusion, the peanut is more than just a snack; it is a complex plant with various parts that serve multiple purposes. From its nutritional benefits to its economic significance and environmental impact, the peanut plays a vital role in many aspects of our lives. Understanding the different parts of the peanut and their uses can help us appreciate this humble legume’s value and potential even more.
Discover ETprotein’s High-Quality Peanut Protein Products
If you’re looking for a reliable source of plant-based protein, ETprotein offers a range of products derived from peanuts and other plant sources. Their peanut protein is an excellent option for those seeking to incorporate more plant-based nutrients into their diet. With ETprotein’s commitment to quality and sustainability, you can trust that you’re getting the best product for your health and the environment.
About ETprotein:
ETprotein, a reputable protein Chinese factory manufacturer and supplier, is renowned for producing, stocking, exporting, and delivering the highest quality organic bulk vegan protein and plant proteins. They include Organic rice protein, clear rice protein, pea protein, clear pea protein, pumpkin seed protein, sunflower seed protein, mung bean protein, peanut protein etc. Their offerings, characterized by a neutral taste, non-GMO, allergen-free attributes, cater to a diverse range of industries. They serve nutraceutical, pharmaceutical, cosmeceutical, veterinary, as well as food and beverage finished product distributors, traders, and manufacturers across Europe, USA, Canada, Australia, Thailand, Japan, Korea, Brazil, and Chile, among others.
ETprotein specialization includes exporting and delivering tailor-made protein powder and finished nutritional supplements. Their extensive product range covers sectors like Food and Beverage, Sports Nutrition, Weight Management, Dietary Supplements, Health and Wellness Products, and Infant Formula, ensuring comprehensive solutions to meet all your protein needs.
As a trusted company by leading global food and beverage brands and Fortune 500 companies, ETprotein reinforces China’s reputation in the global arena. For more information or to sample their products, please contact them and email sales(at)ETprotein.com today.