Pea Protein: Processing Impact on Subunits, Functionality
Discover sustainable pea protein innovations for food. Improve nutrition and functionality. Explore efficient extraction methods and applications. Boost your brand!
Background:
The global demand for protein has been steadily increasing, with approximately one billion people worldwide currently unable to access sufficient protein. In order to address this demand, the partial substitution of animal proteins with plant proteins holds significant merit. Compared to animal proteins, plant proteins, particularly those derived from peas, exhibit environmental friendliness, sustainability, ethical appeal, and a more balanced amino acid composition. Furthermore, the high yield and low environmental requirements of pea protein present a distinct advantage over animal proteins. Peas, as the second most important leguminous crop globally, boast protein with low allergenicity and a balanced amino acid profile, making pea protein a preferred plant-based alternative to animal proteins. However, challenges persist in the food industry due to the inherent beany flavor and processing characteristics of pea protein.
Achievements:
The extraction process of pea protein is crucial for its yield, nutritional content, and functional properties, which, in turn, impact its suitability for various applications in the food industry. Currently, pea protein extraction methods primarily include wet extraction (A), dry fractionation (B), and mild fractionation (C), as illustrated in Figure.
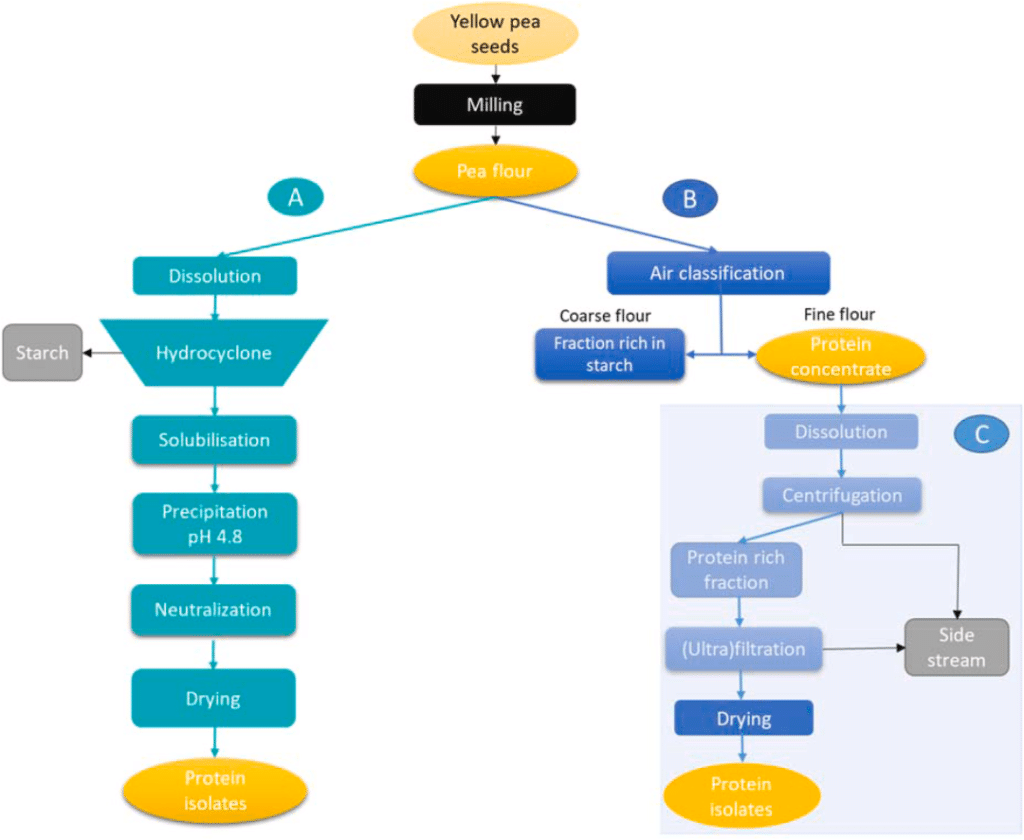
Before extraction, peas undergo preprocessing steps such as cleaning, drying, sorting, dehulling, or splitting to ensure the extraction of pea protein remains unaffected by other components. The oxidation of fatty acids is the primary cause of the beany flavor in pea protein, and this undesirable taste can be mitigated by using supercritical extraction combined with solvent removal of lipids from pea flour. Germination is an effective method for enhancing functionality, nutritional value, processing characteristics, and mitigating undesirable flavors. Research suggests that germination periods exceeding one day may increase bean-related odors, possibly due to increased fatty acid oxidation enzyme activity or the release of legume-related volatile compounds bound to proteins. Fermentation processes with peas can improve protein digestibility, reduce anti-nutrients, and increase mineral bioavailability, making fermentation a promising method for pea processing.
Wet extraction is the prevalent commercial method for pea protein, employing an alkali extraction-isoelectric precipitation process. While wet extraction yields sufficiently pure pea protein, the natural structure and functional properties of the protein are compromised, necessitating further optimization. Dry extraction involves two key steps: milling and air classification. Milling separates protein and starch by grinding pea seeds, but excessive milling intensity can damage starch particles, preventing the separation of protein and starch. Air classification uses air dynamics to separate flour based on particle size, achieving protein-starch separation. Dry extraction is considered environmentally friendly, cost-effective, and sustainable, but it yields lower protein purity. In addition to dry and wet extraction, a mild mixed extraction method involves separating fine components that cannot be separated using dry methods through centrifugation or other purification methods to enhance purity. Post-extraction, protein structures, processing characteristics, and nutritional properties can be improved through subsequent methods such as fermentation, enzymes, chemicals, and heat treatment.
Yellow pea protein consists of albumins (10-20%) and globulins (70-80%). Pea albumin serves as a rich source of essential amino acids, enhancing nutritional value, while pea globulins possess valuable functional properties. Pea protein promotes increased muscle thickness, especially in individuals aiming to enhance muscle strength. Additionally, pea protein exhibits unique functional benefits, including solubility, emulsification, foaming, stability of emulsions and foams, as well as gelation and film-forming capabilities. Incorporating pea protein into staple foods increases protein content and imparts specific functionalities. Reported food applications of pea protein include bread, noodles, baked goods, snacks, meat products, and beverages. Despite improving certain food characteristics, such as enhancing the structure of snacks to make them crispier, challenges persist, such as the beany flavor negatively impacting food ratings and the addition of pea protein reducing the nutritional value of beverages, making them unsuitable for long-term consumption.
Innovation/Application Prospects:
Pea protein represents a promising ingredient in food and beverage research, supplementing dietary protein intake while imparting unique characteristics to food products. However, practical production and processing still face significant challenges, primarily related to sensory and functional properties. Several new formulations and processes have been proposed, showing initial success in meeting food requirements and consumer expectations. Nevertheless, a theoretical foundation is lacking regarding the interactions between pea protein and other components in food matrices. Future directions should focus on researching new technologies to enhance the functional and sensory properties of pea protein, as well as investigating the interactions between pea protein and other components.
Elevate Your Food Innovation with ETprotein’s Premium Pea Protein
In the dynamic landscape of pea protein advancements discussed above, ETprotein stands out as a reliable partner for elevating your food and beverage innovations. Renowned for its commitment to sustainability and superior product quality, ETprotein offers a premium pea protein solution that aligns seamlessly with the global demand for nutritious, plant-based alternatives. Their cutting-edge extraction methods ensure optimal yield, maintaining the natural essence of pea protein without compromising its functional properties. By choosing ETprotein, you empower your brand with a high-quality ingredient, unlocking endless possibilities to create delicious, health-conscious products that captivate consumers. Embrace the future of food innovation with ETprotein’s exceptional pea protein – your key to culinary excellence and market success.
(Note: The translation is provided in a professional tone, and minor adjustments may be needed based on specific context or preferences.)














