Peanut Plant Parts: Anatomy and Functions
-
Table of Contents
- Peanut Plant Anatomy: Exploring Structure and Functions
- Root System: The Foundation of Nutrient Uptake
- Stems: Supporting Growth and Transport
- Leaves: The Photosynthetic Powerhouses
- Flowers: The Beginning of Reproduction
- Fruits and Seeds: The Edible Peanuts
- Conclusion: The Integral Parts of the Peanut Plant
- Discover ETprotein’s High-Quality Peanut Protein Products
Peanut Plant Anatomy: Exploring Structure and Functions
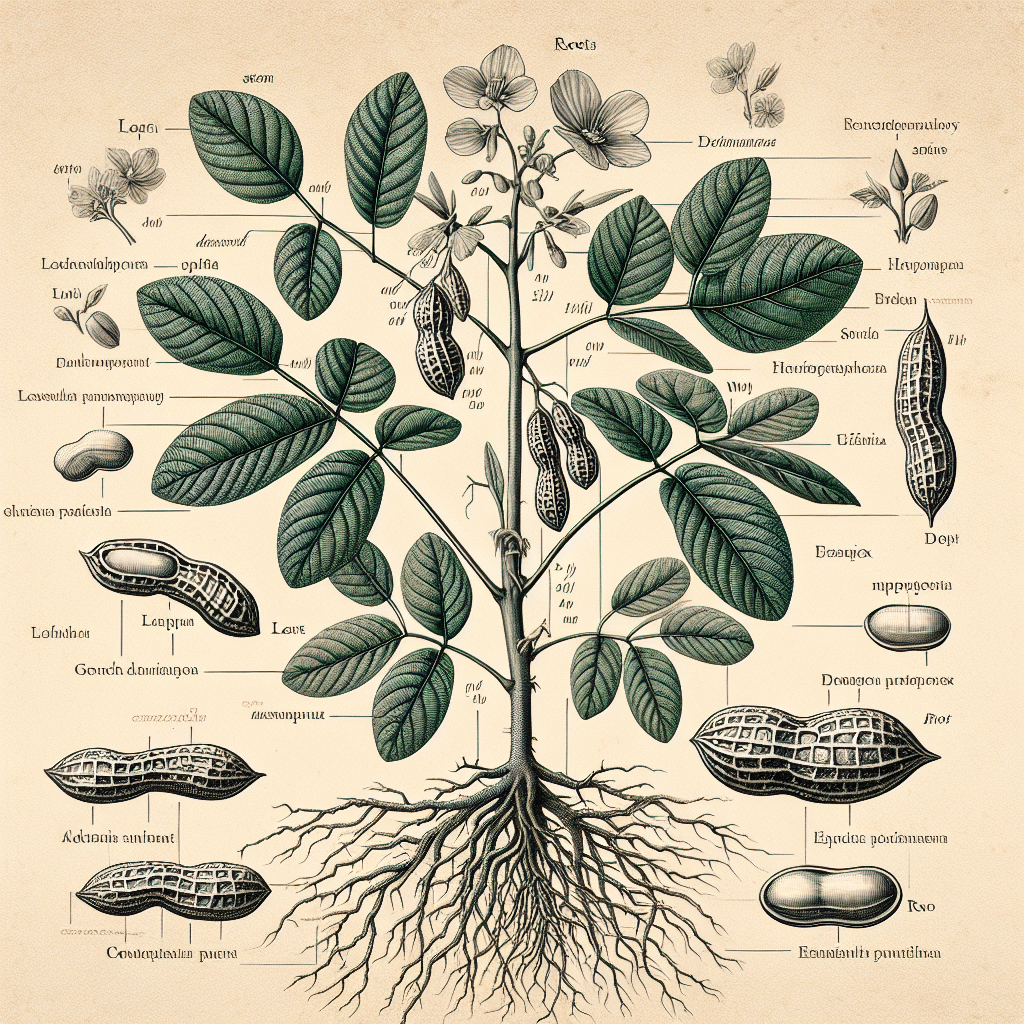
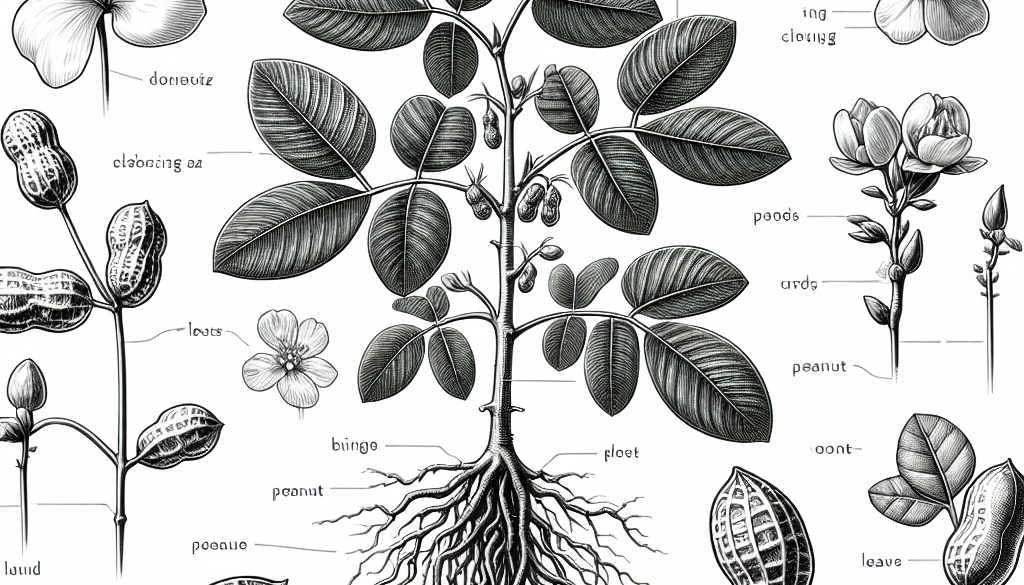
The peanut, or Arachis hypogaea, is a unique legume known for its rich nutritional profile and diverse uses in culinary applications worldwide. Understanding the anatomy and functions of the peanut plant is crucial for agriculturalists, botanists, and food scientists alike. This article delves into the various parts of the peanut plant, elucidating their roles and importance in the plant’s life cycle and productivity.
Root System: The Foundation of Nutrient Uptake
The root system of the peanut plant is fibrous, consisting of a mass of thin roots that spread out into the soil. This network is essential for anchoring the plant and absorbing water and nutrients. The roots also host nitrogen-fixing bacteria, which convert atmospheric nitrogen into a form that the plant can use, enriching the soil in the process.
- Nodulation: Root nodules house symbiotic bacteria that fix nitrogen.
- Water absorption: Fine root hairs increase the surface area for water uptake.
- Nutrient uptake: Roots absorb essential minerals like phosphorus and potassium.
Stems: Supporting Growth and Transport
The peanut plant’s stem is typically short and sturdy, providing support for the leaves and reproductive structures. It also serves as a conduit for the transport of water, nutrients, and sugars between the roots and the aerial parts of the plant.
- Structural support: Stems hold up leaves for optimal sunlight exposure.
- Transportation: Xylem and phloem tissues move water, nutrients, and sugars.
- Pegging: Unique to peanuts, stems produce “pegs” that grow downward into the soil where the peanuts develop.
Leaves: The Photosynthetic Powerhouses
Peanut leaves are typically pinnate with four leaflets and play a crucial role in photosynthesis. They capture sunlight and convert it into chemical energy, which is stored as sugars and fuels the growth of the plant.
- Photosynthesis: Chlorophyll in the leaves captures sunlight to produce energy.
- Transpiration: Stomata on the leaf surface regulate water loss and gas exchange.
- Shade tolerance: Peanut leaves can adjust to varying light conditions, making them efficient even under partial shade.
Flowers: The Beginning of Reproduction
Peanut flowers are bright yellow and typically self-pollinating. After pollination, a fascinating process called geocarpy begins, where the flower’s ovary elongates to form a peg that burrows into the soil, where the peanut will develop.
- Self-pollination: Flowers contain both male and female parts, promoting self-fertilization.
- Geocarpy: The unique reproductive strategy where the fruit develops underground.
- Flower anatomy: Consists of a corolla, calyx, stamens, and a pistil.
Fruits and Seeds: The Edible Peanuts
The fruit of the peanut plant is a legume, not a true nut. The peanut pods develop underground and contain 1 to 4 seeds, or the peanuts themselves. These seeds are rich in oil, protein, and other nutrients, making them a valuable food source.
- Seed composition: Peanuts are composed of a seed coat, cotyledons, and an embryonic plant.
- Nutritional value: High in protein, healthy fats, vitamins, and minerals.
- Harvesting: Peanuts are harvested by pulling the entire plant from the soil and allowing the pods to dry.
Conclusion: The Integral Parts of the Peanut Plant
In conclusion, each part of the peanut plant plays a vital role in its growth, development, and eventual yield of peanuts. From the nitrogen-fixing roots to the photosynthetic leaves, the self-pollinating flowers, and the unique underground fruits, the peanut plant is a marvel of nature’s design. Understanding its anatomy and functions not only fascinates botanists but also aids farmers in optimizing cultivation practices for better harvests.
Discover ETprotein’s High-Quality Peanut Protein Products
If you’re interested in incorporating the nutritional benefits of peanuts into your diet or products, ETprotein offers a range of high-quality peanut protein products. Their peanut protein is ideal for various applications, including sports nutrition, weight management, and general health and wellness products. With ETprotein’s commitment to non-GMO, allergen-free protein sources, you can trust that you’re getting the best plant-based proteins on the market.
About ETprotein:
ETprotein, a reputable protein Chinese factory manufacturer and supplier, is renowned for producing, stocking, exporting, and delivering the highest quality organic bulk vegan protein and plant proteins. They include Organic rice protein, clear rice protein, pea protein, clear pea protein, pumpkin seed protein, sunflower seed protein, mung bean protein, peanut protein etc. Their offerings, characterized by a neutral taste, non-GMO, allergen-free attributes, cater to a diverse range of industries. They serve nutraceutical, pharmaceutical, cosmeceutical, veterinary, as well as food and beverage finished product distributors, traders, and manufacturers across Europe, USA, Canada, Australia, Thailand, Japan, Korea, Brazil, and Chile, among others.
ETprotein specialization includes exporting and delivering tailor-made protein powder and finished nutritional supplements. Their extensive product range covers sectors like Food and Beverage, Sports Nutrition, Weight Management, Dietary Supplements, Health and Wellness Products, and Infant Formula, ensuring comprehensive solutions to meet all your protein needs.
As a trusted company by leading global food and beverage brands and Fortune 500 companies, ETprotein reinforces China’s reputation in the global arena. For more information or to sample their products, please contact them and email sales(at)ETprotein.com today.