Molecular Architects of Protein Synthesis: Unlocking the Secrets of the Cell
-
Table of Contents
Protein Synthesis Flow Chart Explained

Protein synthesis is a fundamental process that occurs in all living organisms. It is the process by which cells build proteins, which are essential for various biological functions. Understanding the steps involved in protein synthesis can provide valuable insights into the intricate workings of cells and the importance of proteins in maintaining life. In this article, we will explore the protein synthesis flow chart and explain each step in detail.
Introduction to Protein Synthesis
Proteins are macromolecules made up of amino acids, and they play a crucial role in the structure and function of cells. They are involved in various processes, such as enzyme catalysis, cell signaling, and structural support. Protein synthesis is the process by which cells create proteins using the information encoded in their DNA.
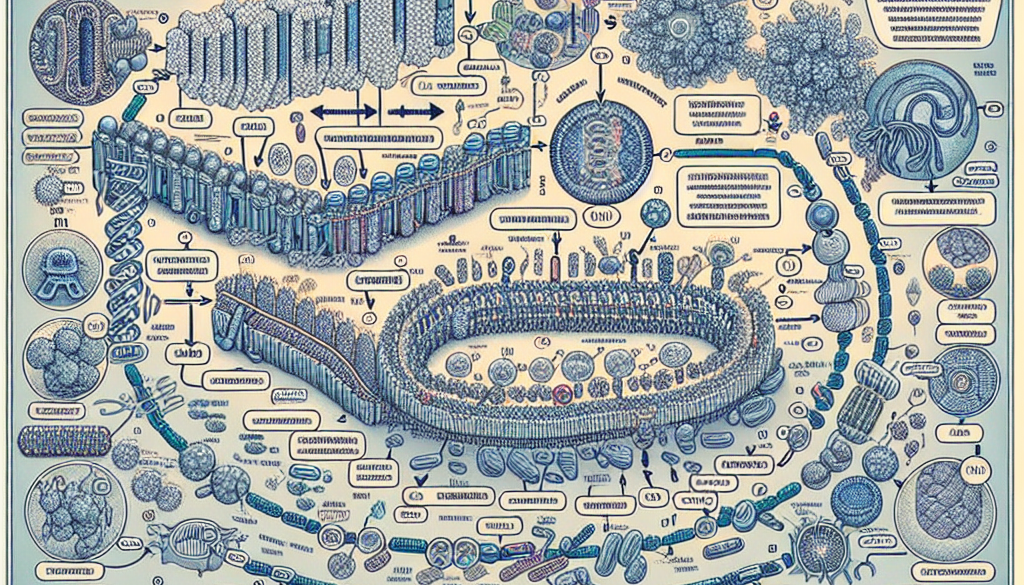
The flow chart of protein synthesis can be divided into two main steps: transcription and translation. Let’s explore each step in detail.
Transcription
Transcription is the first step in protein synthesis, where the information encoded in DNA is transcribed into a messenger RNA (mRNA) molecule. This process takes place in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells and the cytoplasm of prokaryotic cells. The steps involved in transcription are as follows:
- Initiation: Transcription begins when an enzyme called RNA polymerase binds to a specific region of DNA called the promoter. The RNA polymerase unwinds the DNA double helix, exposing the template strand.
- Elongation: The RNA polymerase moves along the template strand, synthesizing a complementary mRNA molecule. The mRNA molecule is built one nucleotide at a time, following the base-pairing rules (A with U, G with C).
- Termination: Transcription ends when the RNA polymerase reaches a specific sequence of DNA called the terminator. The RNA polymerase detaches from the DNA, and the mRNA molecule is released.
Once the mRNA molecule is synthesized, it undergoes further processing, including the addition of a 5′ cap and a poly-A tail. These modifications protect the mRNA molecule and facilitate its transport out of the nucleus.
Translation
Translation is the second step in protein synthesis, where the mRNA molecule is used as a template to synthesize a protein. This process takes place in the cytoplasm of both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. The steps involved in translation are as follows:
- Initiation: Translation begins when the mRNA molecule binds to a ribosome, a complex of proteins and ribosomal RNA (rRNA). The ribosome scans the mRNA molecule until it reaches a specific sequence called the start codon (usually AUG).
- Elongation: The ribosome moves along the mRNA molecule, reading the codons (three-nucleotide sequences) and bringing in the corresponding amino acids. Each codon specifies a particular amino acid, and the ribosome catalyzes the formation of peptide bonds between adjacent amino acids, creating a growing polypeptide chain.
- Termination: Translation ends when the ribosome reaches a stop codon (UAA, UAG, or UGA). At this point, a release factor protein binds to the ribosome, causing the polypeptide chain to be released. The ribosome and mRNA molecule dissociate.
After translation, the newly synthesized polypeptide chain undergoes further modifications, such as folding into its three-dimensional structure and potentially undergoing post-translational modifications, such as phosphorylation or glycosylation.
Summary
Protein synthesis is a complex and highly regulated process that involves the transcription of DNA into mRNA and the translation of mRNA into a protein. The flow chart of protein synthesis can be summarized as follows:
- Transcription: DNA is transcribed into mRNA in the nucleus (eukaryotes) or cytoplasm (prokaryotes).
- Translation: mRNA is translated into a protein in the cytoplasm.
This process is essential for the proper functioning of cells and the synthesis of proteins that carry out various biological functions.
About ETprotein:
ETprotein, a reputable pea protein and rice protein Chinese factory manufacturer and supplier, is renowned for producing, stocking, exporting, and delivering the highest quality organic bulk vegan protein and plant proteins. They include Organic rice protein, clear rice protein, pea protein, clear pea protein, pumpkin seed protein, sunflower seed protein, mung bean protein, etc. Our offerings, characterized by a neutral taste, non-GMO, allergen-free attributes, cater to a diverse range of industries. We serve nutraceutical, pharmaceutical, cosmeceutical, veterinary, as well as food and beverage finished product distributors, traders, and manufacturers across Europe, USA, Canada, Australia, Thailand, Japan, Korea, Brazil, and Chile, among others.
Our specialization includes exporting and delivering tailor-made protein powder and finished nutritional supplements. Our extensive product range covers sectors like Food and Beverage, Sports Nutrition, Weight Management, Dietary Supplements, Health and Wellness Products, and Infant Formula, ensuring comprehensive solutions to meet all your protein needs.
As a trusted company by leading global food and beverage brands and Fortune 500 companies, ETprotein reinforces China’s reputation in the global arena. For more information or to sample our products, please contact us and email sales(at)ETprotein.com today.