What Crop Does Peanuts Come From: Unearthing The Agricultural Roots
-
Table of Contents
- Peanuts: Unveiling the Agricultural Origins of a Beloved Crop
- The Botanical Background of Peanuts
- Understanding Geocarpy
- Historical Cultivation of Peanuts
- Spread Across Continents
- Modern Peanut Farming Practices
- Challenges in Peanut Agriculture
- The Nutritional and Economic Impact of Peanuts
- Economic Significance
- Case Studies and Statistics
- Conclusion: The Enduring Legacy of Peanuts
- Discover ETprotein’s High-Quality Peanut Protein Products
Peanuts: Unveiling the Agricultural Origins of a Beloved Crop
Peanuts, also known as groundnuts, are a staple in diets around the world, cherished for their rich flavor and nutritional profile. But what crop do these versatile legumes come from, and how did they become such an integral part of agriculture and cuisine? This article delves into the fascinating journey of peanuts from their ancient roots to modern-day fields, exploring the plant’s biology, cultivation, and global impact.
The Botanical Background of Peanuts
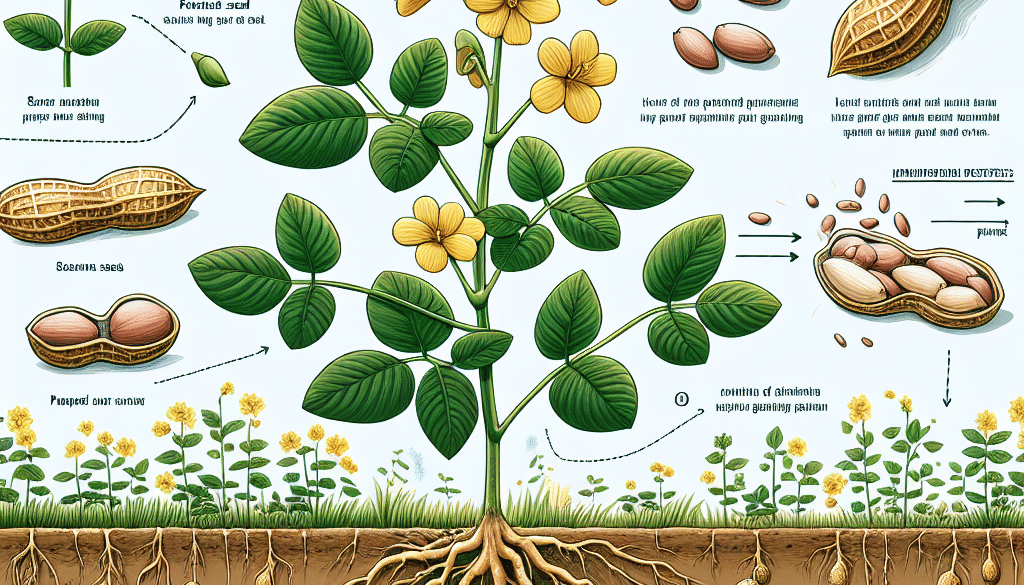
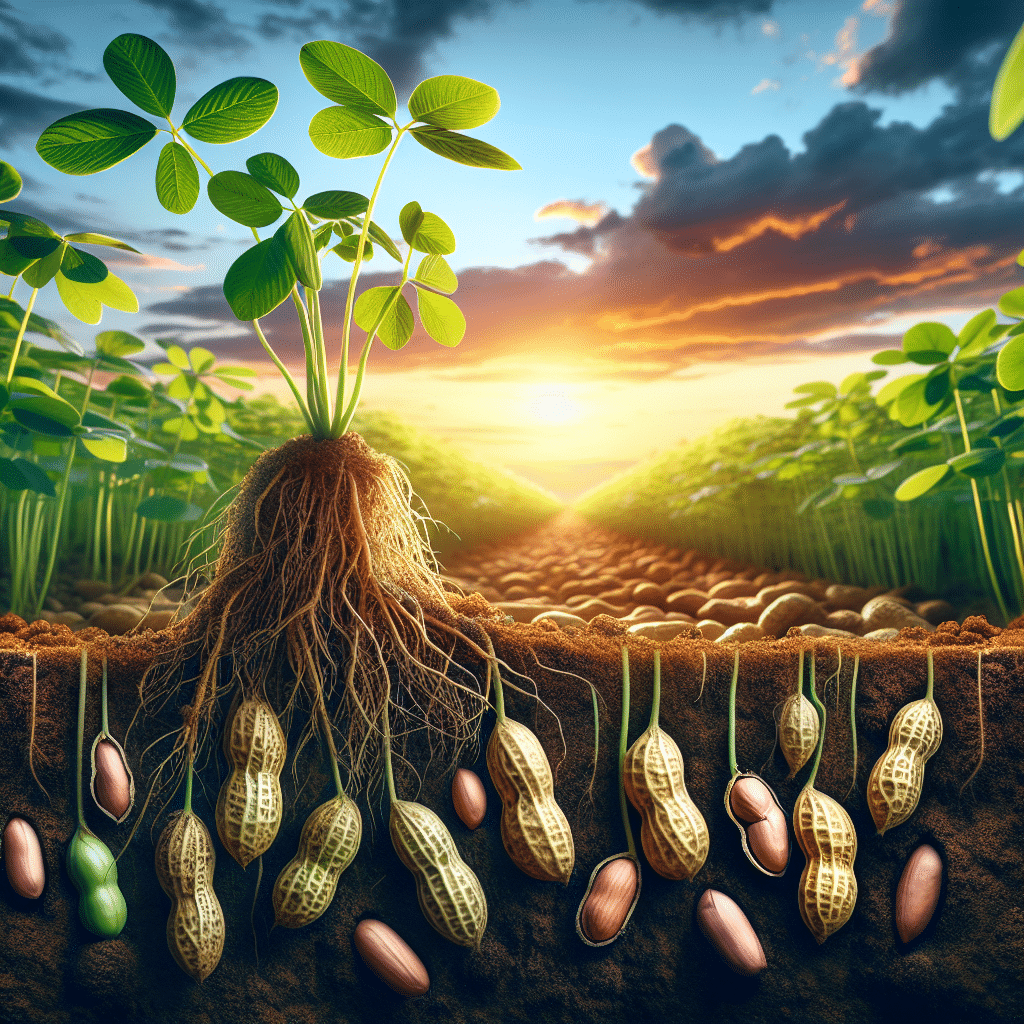
The peanut, scientifically known as Arachis hypogaea, is a legume crop grown primarily for its edible seeds. Contrary to popular belief, peanuts are not true nuts but belong to the legume family, which includes beans, lentils, and soy. They are unique among legumes because they flower above the ground, but the peanuts themselves develop underground, a process known as geocarpy.
Understanding Geocarpy
After a peanut plant flowers, its petals fall off as the fertilized ovary begins to enlarge. The growing ovary, or “peg,” extends and bends toward the ground, eventually burrowing beneath the soil’s surface. The peanut matures in a pod, protected by the earth, which is why it’s sometimes called a groundnut.
Historical Cultivation of Peanuts
Peanuts have a rich history that dates back thousands of years. Archaeological evidence suggests that ancient South American cultures were the first to cultivate peanuts around 7,600 years ago. These early farmers recognized the value of peanuts as a nutrient-dense food source and utilized them in trade and as a staple in their diets.
Spread Across Continents
The cultivation of peanuts spread from South America to other parts of the world through various means, including European explorers who brought them to Africa and Asia. In Africa, peanuts quickly became integrated into traditional farming systems and cuisine. Later, during the transatlantic slave trade, peanuts were brought to North America, where they gained popularity, especially in the southern United States.
Modern Peanut Farming Practices
Today, peanuts are cultivated in warm climates around the globe, with China, India, and the United States being the top producers. The process of growing peanuts involves several critical steps to ensure a successful harvest.
- Soil Preparation: Farmers must prepare the soil carefully to provide the best environment for peanut pods to develop underground.
- Sowing: Peanut seeds are planted after the last frost when the soil has warmed sufficiently.
- Cultivation: The plants require regular weeding and pest management to thrive.
- Harvesting: Peanuts are typically harvested in the fall when the leaves begin to yellow, and the inner shells have a distinct netted pattern.
Challenges in Peanut Agriculture
Despite advancements in agricultural technology, peanut farmers face challenges such as disease management, particularly fungal infections like aflatoxin, which can contaminate peanuts and pose health risks. Crop rotation and other sustainable farming practices are essential in mitigating these issues.
The Nutritional and Economic Impact of Peanuts
Peanuts are not only a delicious snack but also a nutritional powerhouse, packed with protein, healthy fats, vitamins, and minerals. They play a significant role in food security, especially in developing countries where they can be a critical source of nutrition.
Economic Significance
The global peanut industry also has a substantial economic impact. It provides livelihoods for millions of farmers and workers involved in cultivation, processing, and distribution. Peanuts are used in a variety of products, from peanut butter to oil and animal feed, making them a versatile and valuable commodity in international trade.
Case Studies and Statistics
Several case studies highlight the importance of peanuts in agriculture. For instance, in the United States, the peanut industry contributes over $4 billion annually to the economy and supports thousands of jobs. In countries like Senegal and Sudan, peanuts serve as a vital export crop, supporting local economies and providing a source of income for farmers.
Conclusion: The Enduring Legacy of Peanuts
The humble peanut has come a long way from its origins in South America to becoming a global agricultural mainstay. Its unique growth process, historical significance, and nutritional value make it an essential crop that continues to shape diets and economies worldwide. As we’ve explored the agricultural roots of peanuts, it’s clear that this crop will remain a staple for generations to come.
Discover ETprotein’s High-Quality Peanut Protein Products
If you’re interested in incorporating the nutritional benefits of peanuts into your diet or products, ETprotein offers a range of high-quality peanut protein options. Their peanut protein is ideal for enhancing the protein content in various applications, from sports nutrition to health and wellness products.
About ETprotein:
ETprotein, a reputable protein Chinese factory manufacturer and supplier, is renowned for producing, stocking, exporting, and delivering the highest quality organic bulk vegan protein and plant proteins. They include Organic rice protein, clear rice protein, pea protein, clear pea protein, pumpkin seed protein, sunflower seed protein, mung bean protein, peanut protein etc. Their offerings, characterized by a neutral taste, non-GMO, allergen-free attributes, cater to a diverse range of industries. They serve nutraceutical, pharmaceutical, cosmeceutical, veterinary, as well as food and beverage finished product distributors, traders, and manufacturers across Europe, USA, Canada, Australia, Thailand, Japan, Korea, Brazil, and Chile, among others.
ETprotein specialization includes exporting and delivering tailor-made protein powder and finished nutritional supplements. Their extensive product range covers sectors like Food and Beverage, Sports Nutrition, Weight Management, Dietary Supplements, Health and Wellness Products, and Infant Formula, ensuring comprehensive solutions to meet all your protein needs.
As a trusted company by leading global food and beverage brands and Fortune 500 companies, ETprotein reinforces China’s reputation in the global arena. For more information or to sample their products, please contact them and email sales(at)ETprotein.com today.