What Is Soy Protein Made Of? The answer
Table of Contents
- Soy Protein: A Comprehensive Guide to Its Composition and Benefits
- Understanding the Basics of Soy Protein
- The Composition of Soy Protein
- How Is Soy Protein Made?
- Health Benefits and Considerations
- Case Studies and Statistics
- Conclusion: The Role of Soy Protein in Modern Diets
- Discover ETprotein’s High-Quality Soy Protein Products
Soy Protein: A Comprehensive Guide to Its Composition and Benefits
Soy protein has become a staple in the diets of many health-conscious individuals, vegetarians, and those with dietary restrictions. As a plant-based protein source, it offers a variety of health benefits and serves as an alternative to animal-derived proteins. This article delves into the composition of soy protein, its manufacturing process, health implications, and its role in modern diets.
Understanding the Basics of Soy Protein
Soy protein is derived from soybeans, which are legumes native to East Asia. They have been a part of human diets for thousands of years, particularly in Asian cuisines. Soybeans are not only rich in protein but also contain significant amounts of vitamins, minerals, and dietary fiber.
The Composition of Soy Protein
Soy protein is made up of all the essential amino acids required by the human body, making it a complete protein source. The primary components of soy protein include:
- Essential Amino Acids: These are amino acids that the body cannot synthesize on its own and must be obtained through diet. Soy protein contains all nine essential amino acids in adequate proportions.
- Non-Essential Amino Acids: These are amino acids that the body can produce. Soy protein also provides a good balance of these amino acids.
- Isoflavones: These are phytoestrogens found in soybeans that have been linked to various health benefits, including a reduced risk of heart disease and certain cancers.
- Fiber: Soybeans contain both soluble and insoluble fiber, which are beneficial for digestive health.
- Vitamins and Minerals: Soybeans are a good source of B vitamins, vitamin E, phosphorus, potassium, zinc, and iron.
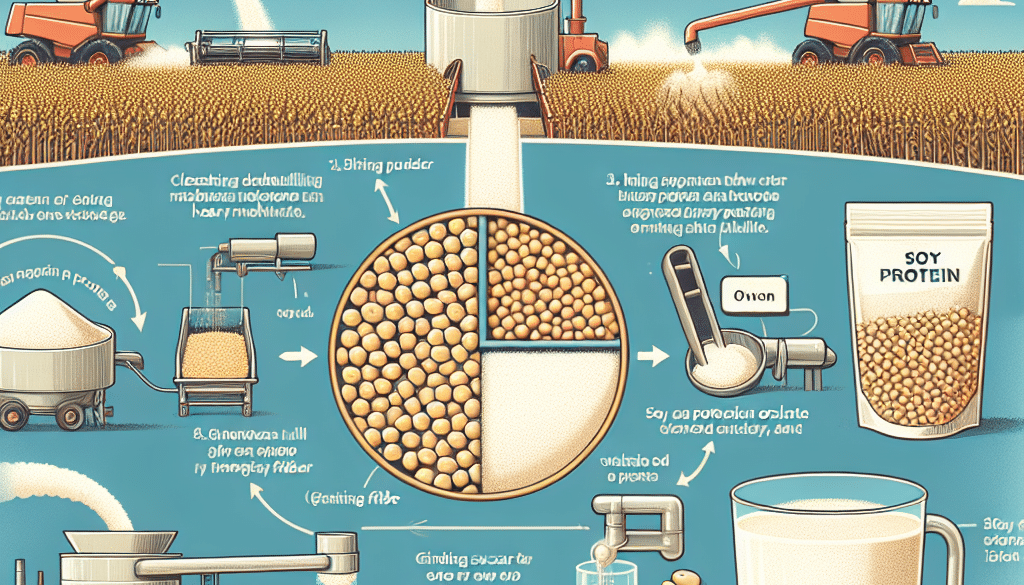
How Is Soy Protein Made?
The process of making soy protein involves several steps to extract the protein from the soybeans:
- Cleaning and Dehulling: The soybeans are cleaned and the hulls are removed to prepare them for processing.
- Crushing: The dehulled soybeans are then crushed to separate the oil from the protein-rich meal.
- Defatting: The soybean meal is further processed to reduce its fat content, resulting in a defatted soy flour.
- Protein Isolation: The defatted soy flour undergoes a water wash or an alcohol wash to remove carbohydrates and fibers, leaving behind a concentrated soy protein isolate.
- Drying: The isolated soy protein is then dried and turned into a powder form for use in various food products.
This process results in three main types of soy protein products:
- Soy Protein Isolate: The most refined form of soy protein, containing about 90% protein. It is used in protein shakes, meal replacements, and health supplements.
- Soy Protein Concentrate: Contains about 70% protein and retains more of the natural fibers. It is often used in baked goods, cereals, and some meat products.
- Textured Soy Protein (TSP): Also known as textured vegetable protein (TVP), TSP is made by forming the concentrate into a textured product that resembles ground meat. It is commonly used as a meat substitute in vegetarian and vegan dishes.
Health Benefits and Considerations
Soy protein offers numerous health benefits, including:
- Heart Health: Studies have shown that soy protein can lower LDL cholesterol levels, potentially reducing the risk of heart disease.
- Weight Management: High-protein diets that include soy protein may aid in weight loss and maintenance by promoting satiety and preserving lean muscle mass.
- Bone Health: The isoflavones in soy protein may help prevent bone loss and promote bone health, particularly in postmenopausal women.
- Cancer Prevention: Some research suggests that soy protein may have protective effects against certain types of cancer, such as breast and prostate cancer.
However, there are also considerations to keep in mind:
- Allergies: Soy is one of the eight major food allergens, and individuals with soy allergies should avoid soy protein.
- Thyroid Function: Excessive consumption of soy protein may affect thyroid function, particularly in individuals with pre-existing thyroid issues.
- Quality of Soy: It’s important to choose non-GMO and organic soy products to avoid potential health risks associated with genetically modified organisms and pesticides.
Case Studies and Statistics
Several studies have highlighted the benefits of soy protein. For instance, a meta-analysis published in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition found that soy protein intake was associated with a significant decrease in serum cholesterol levels. Additionally, the FDA has recognized the cholesterol-lowering effects of soy protein and allows health claims for products containing soy protein.
According to market research, the global soy protein market size was valued at USD 8.91 billion in 2020 and is expected to grow, reflecting the increasing demand for plant-based proteins.
Conclusion: The Role of Soy Protein in Modern Diets
Soy protein is a versatile and nutritious component of many diets. Its complete amino acid profile, health benefits, and functionality as a meat substitute make it an attractive option for those looking to diversify their protein sources. Whether incorporated into shakes, meat alternatives, or baked goods, soy protein offers a sustainable and healthful choice for consumers worldwide.
Discover ETprotein’s High-Quality Soy Protein Products
If you’re looking for premium soy protein products, ETprotein offers a range of organic, non-GMO options that cater to various dietary needs. Their soy protein isolates and concentrates are perfect for enhancing your food products with a neutral taste and allergen-free attributes. With a commitment to quality and customer satisfaction, ETprotein is your go-to source for plant-based protein solutions.
About ETprotein:
ETprotein, a reputable protein and L-(+)-Ergothioneine (EGT) Chinese factory manufacturer and supplier, is renowned for producing, stocking, exporting, and delivering the highest quality organic bulk vegan proteins and L-(+)-Ergothioneine. They include Organic rice protein, clear rice protein, pea protein, clear pea protein, watermelon seed protein, pumpkin seed protein, sunflower seed protein, mung bean protein, peanut protein, and L-(+)-Ergothioneine EGT Pharmaceutical grade, L-(+)-Ergothioneine EGT food grade, L-(+)-Ergothioneine EGT cosmetic grade, L-(+)-Ergothioneine EGT reference grade and L-(+)-Ergothioneine EGT standard. Their offerings, characterized by a neutral taste, non-GMO, allergen-free attributes, with L-(+)-Ergothioneine purity over 98%, 99%, cater to a diverse range of industries. They serve nutraceutical, pharmaceutical, cosmeceutical, veterinary, as well as food and beverage finished product distributors, traders, and manufacturers across Europe, USA, Canada, Australia, Thailand, Japan, Korea, Brazil, and Chile, among others.
ETprotein specialization includes exporting and delivering tailor-made protein powder and finished nutritional supplements. Their extensive product range covers sectors like Food and Beverage, Sports Nutrition, Weight Management, Dietary Supplements, Health and Wellness Products, and Infant Formula, ensuring comprehensive solutions to meet all your protein needs.
As a trusted company by leading global food and beverage brands and Fortune 500 companies, ETprotein reinforces China’s reputation in the global arena. For more information or to sample their products, please contact them and email sales(at)ETprotein.com today.